Table of contents
- Introduction to BENQI (QI)
- What Is the Significance of BENQI?
- The BENQI (QI) Token
- Making Use of the BENQI Protocol
- Earning on the Protocol
- BENQI Borrowing Parameters
- Collateral Factor
- Reserve Factor
- Close Factor
- Liquidation Incentive
- Models of Interest Rates
- How Funds Are Stored
- Risks
- Smart Contracts Risks
- Liquidation Risks
Introduction to BENQI (QI)
Avalanche was chosen because of its decentralized network’s purported great scalability, low fees, and compatibility with popular plugin wallets, according to the team. One of BENQI’s ambitions is to become a cross-chain center, with the Avalanche subnets connecting Ethereum, Polkadot, and Binance Smart Chain (BSC).
BENQI was established in 2021 with a $6 million investment with key investors including Ascensive Assets, Dragonfly Capital, Mechanism Capital, Arrington XRP Capital, Spartan Group, TRGC, Woodstock Fund, Ava Labs, Morningstar Ventures, GBV Capital, Skynet Trading Ltd, Rarestone Capital, Moon Inc., and Genblock Capital.
What Is the Significance of BENQI?
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) has exploded in popularity during the last two years. Because the majority of DeFi’s activity is now conducted on Ethereum, the network has begun to encounter congestion, resulting in hefty network fees. This has proven to be a substantial obstacle for both new and old DeFi users with little financial resources to justify their participation.
As a result, by delivering a Liquidity Market Protocol on a highly scalable and decentralized platform, BENQI hopes to solve these issues. BENQI will democratize access to decentralized financial products by providing permissionless lending and borrowing, with a focus on approachability, ease of usage, and cheap fees. This means users can:
- Supply and withdraw liquidity from a shared liquidity market in real-time.
- Borrow money right away from a liquidity market by pledging their assets as security.
- Have a real-time, transparent picture of interest rates based on the asset’s market supply and demand 24 hours a day, 7 days a week.
The BENQI (QI) Token
The QI token is a native asset on Avalanche that supervises the whole BENQI protocol ecosystem, including future revisions. Through BENQI Improvement Proposal (BIPs), QI is obliged to vote and decide on the outcome of proposals. The protocol will be run by the founding team at first, but will eventually be handed over to a Decentralized Autonomous Organization (DAO).
Additionally, holders of the QI token will be able to initiate ideas and vote on topics that will guide the protocol’s direction as part of the DAO. QI has a total supply of 7,200,000,000 tokens. Market participants that actively participate with the platform will get QI tokens as part of the token distribution. The Liquidity Mining software will disperse the bulk of the tokens.
Making Use of the BENQI Protocol
First and foremost, to use the protocol, the user must first deposit an asset that the protocol accepts. Users will be able to earn interest on their borrowings based on the asset’s market demand. Therein, deposited assets can also be used as collateral to enable the user to borrow further assets. Depositing funds earn interest, which offsets the compounded interest rates from borrowing.
As the platform grows, more token pools will be added. Additional pools will be approved based on community votes and recommendations, utilizing the QI governance token, when the protocol’s governance evolves into a Decentralized Autonomous Organization (DAO).
The following are some examples of parameters that could be voted on:
- Model of Interest Rates
- The incorporation of assets that meet the protocol’s
- Risk requirements Overcollateralization and liquidation
- Modifications to the Liquidity Mining Program to adjust incentives in response to market conditions Updates to the protocol, such as smart contract changes and governance processes
Earning on the Protocol
You can start earning interest on your assets today. Depositors will earn continual interest on their assets, which will adjust algorithmically dependent on market conditions. Each asset has its own supply and demand market, as well as an APY (Annual Percentage Yield) that fluctuates over time.
The QiToken is a representation of the asset balance provided to the BENQI protocol by the user. It is received in the wallet in exchange for delivering assets to the protocol, and it works to accrue value relative to the initial asset via the token’s interest rate.
The underlying item submitted to the protocol will be used to create QiTokens (e.g: QiAVAX, QiLINK, QiWBTC, QiUSDT, etc.). Even if the number of QiTokens in the wallet remains constant, QiTokens are convertible into an increasing amount of the original asset.
BENQI Borrowing Parameters
Instead of selling the asset, the user would be able to borrow it using the current asset placed in the protocol. This gives liquidity (working capital) to the user without requiring them to liquidate their current asset.
Before borrowing, the user must deposit an acceptable asset that will be used as collateral. Interestingly, there is no fixed time to repay back loans. Borrowing can be done for an undefined period as long as the user’s position is safe (Health).
Here are the borrowing protocol parameters:
Collateral Factor
The maximum that may be borrowed on a specific asset, for example, the AVAX collateral factor is 40%, thus if AVAX costs $100, the maximum that can be borrowed in other assets is $40.
Reserve Factor
The percentage of the borrower’s interest that goes to the BENQI protocol and can be removed through governance, for example, a reserve factor of 20% means that 20% of the asset’s interest goes to the protocol.
Close Factor
The maximum amount that can be liquidated in a single transaction, for example, a 50 percent close factor means that a single liquidate transaction can only repay 50 percent of a liquidatable account’s borrowings.
Liquidation Incentive
This is the incentive given to liquidators to conduct liquidations and maintain the protocol solvent, For instance, a 10% liquidation incentive means liquidators will get an additional 10% of the borrower’s collateral for the liquidation transaction.
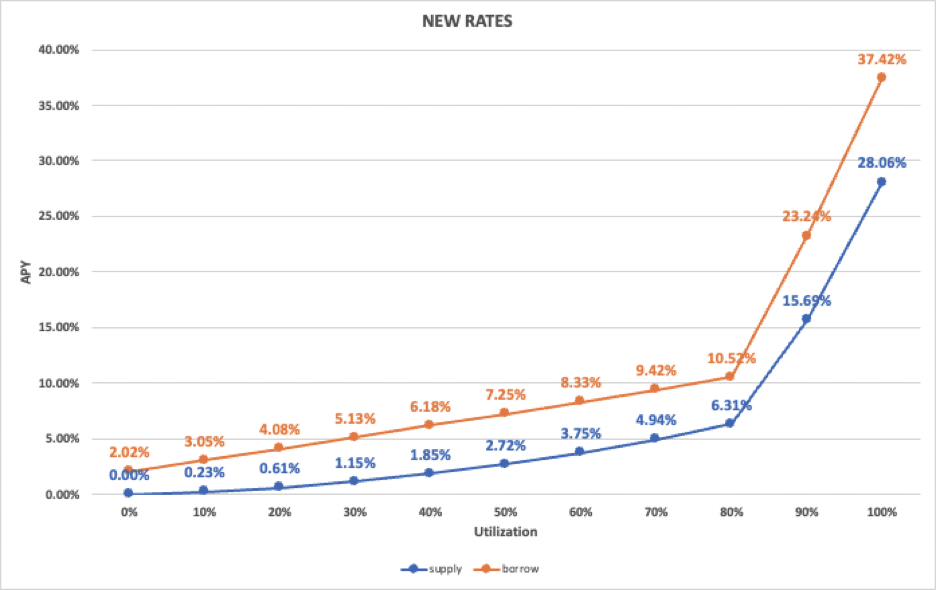
Models of Interest Rates
In BENQI, all interest rates are calculated as a function of a statistic called the utilization rate. The utilization rate, which is simply the percentage of total asset borrowed out versus total asset supplied, determines the interest rates on BENQI. A high utilization rate suggests that there has been a significant amount of borrowing, whilst a low ratio indicates the contrary.
The interest rates of each asset market are continually adjusted by BENQI’s interest rate models based on the utilization rate. A high ratio would result in larger interest payments from borrowers and, as a result, higher interest payments to suppliers, encouraging suppliers to add more assets to the protocol and assuring adequate liquidity levels.

BENQI presently employs a Linear Rate model for the majority of its assets, but will soon switch to a Jump Rate model. When it comes to rewarding liquidity, the Jump Rate Model is more effective.
How Funds Are Stored
Smart Contracts are in charge of managing funds. Depositors and lenders will receive tokenized yield-bearing tokens (QiTokens) that can be used to withdraw funds from the pool on-demand. On Avalanche, QiTokens can be transferred and exchanged just like any other cryptocurrency.
Risks
There is no such thing as a risk-free system in the blockchain world. Smart Contract and Liquidation Risks are two potential dangers associated with the protocol. By conducting audits and keeping the protocol public and open source, the team has taken the required efforts to reduce these risks as much as feasible.
Smart Contracts Risks
The protocol will interact with a variety of smart contracts, each of which carries its own set of hazards. This can include both known and unknown risks that could cause the smart contracts to fail or become vulnerable, resulting in assets being locked or lost forever.
Liquidation Risks
Due to the systemic risks of the issuing platforms or market volatility, the value of assets supplied or borrowed on the protocol may change, including the loss of peg of some pegged assets. A user’s stake could be liquidated or closed as a result of this.
Disclaimer: The views and opinions expressed in this article are solely the author’s and do not necessarily reflect the views of CoinQuora. No information in this article should be interpreted as investment advice. CoinQuora encourages all users to do their own research before investing in cryptocurrencies.