Matic Network, now called Polygon is a protocol for connecting Ethereum compatible blockchain networks and provides a protocol to build such a blockchain. Ethereum blockchain has been a widely popular choice among crypto users and developers. The mass attention it has captured has created a significant user base for some of its decentralized applications. Ethereum is supported by an impressive developer community and ecosystem. But it is certainly affected by a great deal of user experience issues. Some of these include low scalability, high transaction fees, slow transaction confirmation, and poor usability.
Other limitations of Ethereum like delayed transaction finality, non-customizable tech stack, and governance dependence also affect its usability in real-world applications.
To provide a better experience to their users, projects are exploring alternative blockchains which are compatible with Ethereum. However, there is no specialized framework to build such blockchains. Very few protocols are being developed to connect these blockchains with Ethereum.
Polygon is an off/side chain scaling solution for blockchains to provide scalability and superior user experience to dApps/user functionalities. It allows near-instant transfers, exchange, and conversion of digital assets and cryptocurrencies. Matic foundation intends to provide Matic wallet, payment APIs & SDKs, products, identity solutions, and other enabling solutions that will allow developers to design, implement and migrate dApps built on base platforms like Ethereum. It has built high-quality user experience mobile and web browser libraries that will enable businesses to create real-world, end-user applications on a large scale.
Image source: Polygon
Some blockchain projects which use Polygon protocol are Polymarket, Aavegotchi, Decentral Games, SportX, Easyfi, Neon District among others.
Features
Currently, Ethereum is the first base chain that Matic Network securely integrates with, using an adapted implementation of the Plasma framework. In addition, the Matic network intends to integrate multiple leading smart contract platforms cryptocurrencies to provide a universal platform for the users to be able to use/exchange their assets from various blockchains. It provides:
- a set of modules for developing custom blockchains.
- security service.
- an interoperability protocol for exchanging messages between Ethereum and other blockchains.
- adaptor modules for enabling interoperability for existing blockchains.
- fraud-proof mechanism.
Architecture
Polygon network follows a dual strategy of proof of stake to provide consensus. It consists of stakers who need to stake tokens. They validate the transactions and propose checkpoints on the mainchain using the PoS consensus mechanism with a ⅔ majority. They also choose block producers amongst themselves, to produce blocks on the side chains. Block producers have to provide a significant stake to be nominated. It uses PoS at the checkpointing layer and block producers at the block producer layer to achieve faster block time while ensuring a high degree of decentralization.
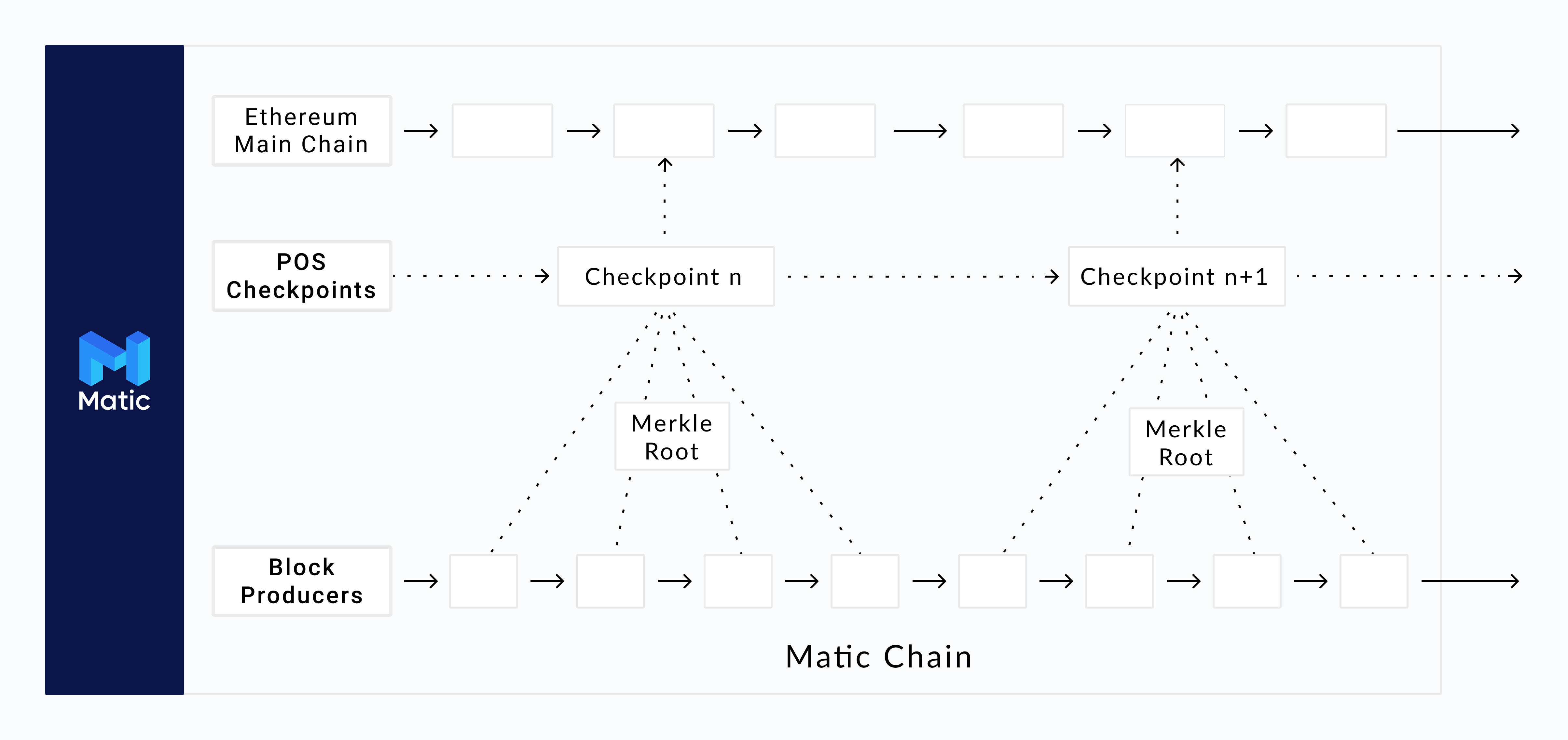
The Matic Network public checkpointing layer supports multiple side chains by design. Businesses can have their dedicated side chains connected to the public checkpointing layer having full control of their execution environments, while still retaining the immutability, probability, and security of transactions via the checkpointing mechanism. The movement of the assets from one chain to another will be managed at the checkpointing layer and may not require any interaction with the mainchain.
The Polygon Network solves slow transaction issues by using a high throughput blockchain with consensus provided by block producers. It then uses a Proof Of Stake layer to validate the blocks and publish periodic proofs which are Merkle roots of the blocks produced by the block producers to the Ethereum mainchain. This helps in achieving a high level of decentralization while maintaining extremely fast (< 2 seconds) block confirmation times.
In the future, Polygon is expected to be able to easily add more side chains horizontally to increase the total number of transactions on the Matic Chain while using the same decentralized PoS layer.
The ever-increasing size of blockchain results in fewer full nodes supporting the public chains, which risks centralization. For the Matic Network, the primary layer which provides decentralization may choose to store only the blocks of the Matic Chain from the previous checkpoint to the next checkpoint. All previous transaction/block proofs have been submitted to the mainchain. This enables extremely low fidelity PoS nodes which can be run in very low-cost machines with low storage. In the future, Polygon intends to enable mobile device-based PoS miners too.
Compatibility With Ethereum
Any valid Ethereum address is a valid Matic address and a receiver does not need to be on the Matic chain to receive payment. They would only need to have a Matic Wallet when they want to retrieve the payments on the main chain or spend them in the ecosystem on the Matic Network.
The Matic Network uses a standard EVM-based state machine, which is run by the Block Producer nodes to generate blocks. it becomes very easy to port DApps and smart contracts running on the Ethereum blockchain to the Matic Network.
Matic Token will be issued as ERC-20 standard-compliant digital tokens on the Ethereum blockchain. These would be utility tokens that function as the unit of payment and settlement between participants on the Matic Network. Matic tokens will be used as the unit of exchange to quantify and pay the costs of the consumed computational resources.
Matic Contracts
The Matic smart contracts deployed on the mainchain (currently, Ethereum) provide the core logic for the Matic Network. The contracts contain various mechanisms such as deposits and exits from the main chain to the sidechain and vice versa. They also contain the exit priority queue, the periodic state commitments from the Validator layer, fraud-proof mechanisms, bonded exit challenge logic, and various other components.
Components
Matic Deposit Bridge:
The bridge(s) of the Matic Network is part of block producer nodes that listen to the RootContract events on the mainchain and monitor any token/ether transfer events happening to the RootContract. This bridge utilizes Matic Network’s tool named Dagger. Once the bridge detects a deposit on the mainchain, it fires a Deposit event on the Matic chain and the user’s address on the Matic Network is allocated the deposited amount.
Matic Withdrawl Bridge:
When an address on the Matic Network submits a withdrawal request to the network, the corresponding tokens are burnt on the Matic chain and this transaction is pushed onto the Matic chain. After the specified checkpoint interval, the PoS checkpoint layer will publish the checkpoint to the main chain, which will include the proof of burn i.e. withdrawal of these tokens on the Matic chain. Once this checkpoint is committed on the mainchain, the user can claim their withdrawn tokens.
Use Cases
The Polygon network will provide an interface for users, payment APIs, and SDKs for DApps, merchants, and users to instantly accept or pay in crypto assets (e.g., ERC20 tokens, Ethers, ERC721 tokens). Third parties can use the Polygon network to exchange any tokens for other tokens by leveraging the Ox liquidity pool or other liquidity providers while transferring crypto assets.
The Matic Network is expected to provide faster and cheaper trades for an exchange platform. This makes it capable of supporting decentralized exchanges and enabling trust-less, reliable, and easy crypto trades.
The Matic Network will enable platforms for merchants to assess the creditworthiness of connected users via their transaction history. This enables merchants to lend tokens to users on the network when transacting with users that do not have sufficient funds. The Matic Network expects to use the Dharma protocol to provide tokenized debt to users.
Games are expected to be a big part of the Polygon network. In-game assets represented as NFTs (ERC721) are expected to be bought, sold, and traded in huge numbers on its side chains. The Matic Development Team already has started building infrastructure for developers, starting with Dagger. Dagger is a tool or engine to track Ethereum accounts and events in real-time.
Developers can use Dagger to track their own smart contracts, accounts, and transactions. They can create custom services or integrate with third-party services through IFTTT or Zapier.
The polygon development team is also working on building an easy-to-use Plasma wallet mobile app, integrated with WalletConnect, to ensure secure storage of keys, intuitive access to the features provided by the Matic Network, as well as a seamless mechanism to connect browser-based DApps to the mobile app. Users can interact with DApps on browsers and in the future many more devices, while still keeping their keys secure in their mobile wallets. This wallet will act as a ready tool for DApp developers to get their users onboard and working with Matic side chains quickly and efficiently.
 cryptoknowmics.com
cryptoknowmics.com
