The ISO 20022 crypto-list is a collection of compliant digital coins and tokens that satisfy the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) standards 20022. Many cryptocurrencies will be integrated into this new financial system as ISO 20022-compliant cryptocurrencies. There is much speculation that these cryptocurrencies will soar in price once the standard is implemented.
Digital Token Identifiers (DTIs) are identifier numbers or symbols representing digital currencies. The main problem with transacting in digital currencies is that they don’t have identifiers that banks can use to differentiate token transactions. For example, a bank program could easily tell the difference between “USD” and “AUD,” but this is more difficult for “Bitcoin” and “Bitcoin Cash.”
ISO (International Organization for Standardization) is a non-governmental global organization based in Geneva, Switzerland. ISO develops international standards for industrial, commercial, and proprietary use. If an ISO standard is established, virtually all financial institutions worldwide adopt it. An ISO code for Bitcoin (BTC) could facilitate global mainstream adoption more than any other action.
This guide explains some of the basics of ISO 20022 and provides a list of cryptocurrencies compliant with ISO 20022.
What are ISO Standards?
Understanding the intricacies of ISO standards is crucial for businesses, professionals, and stakeholders in various industries. These internationally recognized guidelines, established by the International Organization for Standardization, dictate quality, efficiency, and safety in both products and services worldwide. Grasping what these standards entail and how they influence different sectors can provide a competitive edge, ensuring compliance and fostering trust among consumers and partners.
1. Guaranteeing Quality and Safety Across Industries
ISO standards serve as a seal of assurance, enabling companies to demonstrate that their products meet rigorous standards for quality and safety. For example, widely recognized standards like ISO 9001 for quality management systems signify a company’s commitment to delivering consistent quality, thereby building consumer trust and credibility.
2. Prioritizing Environmental Consciousness
With a global shift towards environmental sustainability, standards such as ISO 14001 are pivotal. They outline criteria for an environmental management system that helps organizations reduce their environmental footprint, ensuring sustainable operational practices that resonate with eco-conscious consumers and stakeholders.
3. Navigating Specialized Industrial Standards
Numerous industries rely on specialized ISO standards tailored to specific products, processes, or sectors. These standards, ranging from ISO/IEC 27001 for information security to ISO 26000 for social responsibility, address unique challenges and operational nuances, helping businesses maintain industry-specific best practices.
4. Harmonizing International Compatibility and Interoperability
One of the unsung benefits of ISO standards is their role in ensuring compatibility across different markets and countries. This standardization is crucial in sectors like technology and telecommunications, where products and services must seamlessly integrate and function globally.
5. Streamlining Global Trade Practices:
ISO standards create a common language in international trade, facilitating smoother transactions and partnerships across borders. By adhering to these internationally recognized practices, businesses can navigate the complexities of global trade with greater ease and confidence.
6. Embracing Evolution Through Continuous Improvement
Staying current is key in a rapidly evolving marketplace. ISO standards are regularly reviewed and updated, allowing businesses to stay relevant and adapt to technological advancements and consumer needs. These periodic updates are instrumental for companies wishing to stay ahead in an ever-changing competitive landscape.
ISO standards undergo a meticulous development process encompassing expert input, rigorous draft reviews, and international consensus from participating members. This comprehensive approach balances established best practices and innovative solutions, catering to current market demands and future trends.
What is ISO 20022?
ISO 20022 is an international protocol that provides a secure and standardized way of exchanging financial messages between organizations within the payment industry. The protocol will replace the 50-year-old SWIFT financial messaging system, which banks and other financial institutions use to facilitate global payments.
The standard addresses the need of financial services organizations looking to create a globally accepted messaging language. The language allows them to implement their business processes and collaborate with their partners utilizing one universal platform.
Financial institutions such as banks, crypto companies, and stock brokers can benefit from ISO 20022. It enables efficient and effective communication across multiple departments and organizations, reducing costs associated with numerous communication systems. In addition, achieving interoperability between existing protocols while still having the ability to support specific financial business processes makes ISO 20022 an excellent choice for any company involved in financial services.
Why is the ISO 20022 Crucial?
Financial institutions have always had to consider technological advances to keep up with the competition. In the new “ISO 20022” standard, cryptos could be assigned ISO codes if they comply with ISO 20022. This could lead to adoption by centralized banks and enable cross-border crypto payments through centralized financial institutions.
As we move toward a new quantum financial system, any third party, including cryptocurrencies, wishing to engage with them must be able to use the ISO 20022 format. The standard presents an essential test for the ability of institutions of all sizes to adapt and embrace innovative solutions.
ISO 20022 is more advanced than the traditional legacy formats banks use in that it supports more significant data volumes and faster processing rates. As a result, it is ideal for quick payments, daily liquidity management, compliance checks, and fraud detection and prevention. Overall, ISO 20022 presents an opportunity and challenge for companies wishing to stay ahead of their peers regarding technology.
Considerations for migrating to ISO 20022
Crypto companies must consider several factors when migrating to the ISO 20022 protocol. These include:
- Readiness of payment infrastructure: The payment infrastructure must be ready to support ISO 20022. The infrastructure includes hardware and software installations and the ability to send and receive messages in the proper format.
- Compliance with regulatory requirements: Organizations must ensure their systems comply with necessary regulations, such as anti-money laundering laws.
- Data security: Data security is a crucial concern regarding payments and financial transactions. Organizations must ensure that their systems are secure and can protect customer data.
- Cost of implementation: Migrating to the ISO 20022 protocol can be costly, so organizations must consider the cost of implementation before deciding if it’s a viable option.
- Program governance and support: Organizations must have a plan to ensure their programs are adequately managed and supported. This includes having a dedicated team, proper monitoring and reporting processes, and adequate staff training.
- Strategic benefits of ISO 20022 implementation: Organizations must consider the strategic benefits of ISO 20022 performance, such as increased efficiency and cost savings.
- Benefits of the ISO 20022 Crypto List: The ISO 20022 Crypto List provides numerous benefits for investors. By listing compliant coins and tokens, it offers a level of assurance that the underlying asset meets specific standards.
- Training and resources requirements: Organizations must adequately train their staff to use the ISO 20022 protocol properly. They should also have access to adequate resources, such as manuals and helpdesks, to ensure proper protocol implementation.
- Client education: Organizations must ensure their clients are aware of the changes to the payment infrastructure and any possible risks associated with using ISO 20022. Client education can help reduce the risk of fraud and other security issues.
- Management of new data and data fields: When migrating to ISO 20022, organizations must also be prepared to manage any new data or data fields that might be required. They include having the necessary processes and systems to process this information.
Compliance with ISO 20022
There has yet to be an official certification authority for ISO 20022 compliance. The ISO 20022 Compliance Checklist provided by the ISO 20022 Registration Authority (RA) and Technical Support Group (TSG) is a guidance document for implementers, adopters, and consumers of ISO 20022 messages. It helps them assess their adherence to the standard and ensure organizations account for the key aspects of ISO 20022 compliance.
Compliance Checklist
This checklist outlines various elements to consider when implementing ISO 20022, such as message structure, data types, message flows, and message versions. The list will help organizations align their implementations with the standard and enhance interoperability.
Here is a list of the key aspects of the checklist, along with a brief description of each:
- Use of official ISO 20022 Message Definitions: The messages must use the official ISO 20022 message definitions published by ISO and available on the ISO 20022 website.
- ISO 20022 Business Transaction: This refers to the business process or transaction the message intends to support. The ISO 20022 standard defines a set of business transactions, and messages should be used according to these definitions.
- Messages must be valid ISO 20022 Message Instances: The messages must conform to the structure and content rules defined by the ISO 20022 standard.
- Messages must respect the ISO 20022 Constraints: These refer to the constraints defined by the ISO 20022 standard, such as maximum length, data type, and allowed values for specific fields.
- Messages must use registered code values: The codes used in messages must come from the code lists registered and maintained by ISO.
- Use of the Business Application Header: The Business Application Header is included in all ISO 20022 messages. It contains information about the message, such as its type, sender, and receiver.
- Use of Supplementary Data Extensions: Supplementary Data extensions allow for additional information in messages not covered by the standard message definitions. These extensions must follow the rules defined by ISO.
While compliance with the checklist does not grant an official certification, it is a valuable tool for self-assessment and ensuring conformity with ISO 20022. Implementers and adopters can use the checklist to verify that they have adequately addressed the essential aspects of ISO 20022 implementation, reducing the risk of misinterpretation or non-compliance.
Additionally, industry-specific organizations and regulatory bodies may develop their guidelines or requirements for ISO 20022 adoption within their domains. Organizations must consider these specific requirements in addition to the general guidance provided by the ISO 20022 Compliance Checklist.
Benefits of Compliance
Compliance with ISO 20022 can offer several benefits for the crypto industry. Here are some of the advantages:
- Standardization and Interoperability: ISO 20022 provides a globally accepted standard for messaging in cross-border payments, including cryptocurrencies. By complying, cryptocurrencies can ensure interoperability and seamless communication between financial systems and institutions. Standardization allows more efficient and secure transfer of funds across different networks, facilitating increased adoption and integration of cryptocurrencies into existing financial infrastructure.
- Enhanced Regulatory Compliance: Compliance can help cryptocurrencies align with regulatory requirements more effectively. As governments and regulatory bodies focus on developing frameworks for digital assets, adhering to international standards like ISO 20022 can demonstrate commitment to regulatory compliance and facilitate engagement with traditional financial institutions. This can improve the perception of cryptocurrencies and increase trust among regulators and traditional market participants.
- Integration with Central Banks and Financial Institutions: Compliance allows global central banks and financial institutions to use cryptocurrencies in centralized settings. Certain cryptocurrencies, such as Ripple ($XRP), $XDC, Stellar Lumens ($XLM), Iota, and Algorand, are already ISO 20022 compliant. Compliance increases the chances of these cryptocurrencies being considered for digital reserve currencies or inclusion in centralized payment systems established by central banks. Such integration can provide greater liquidity, increased transaction volumes, and wider acceptance of these cryptocurrencies.
- Streamlined Cross-Border Payments: ISO 20022 aims to optimize and streamline cross-border payment systems. By complying with this standard, cryptocurrencies can benefit from faster and more cost-effective payment processing, reducing friction and enhancing the efficiency of international transactions. This can make cryptocurrencies more attractive for cross-border commerce and remittances, opening up new use cases and increasing their utility.
- Improved Trust and Transparency: ISO 20022 compliance can enhance trust and transparency within the crypto industry. The standard provides a structured format for payment messages, improving clarity and reducing the risk of errors or misinterpretation. Clear and standardized messaging promotes transparency, reduces fraud risks, and strengthens the overall security of crypto transactions.
It is important to note that the impact of ISO 20022 compliance on the crypto industry is still evolving, and the full extent of the benefits will become clearer as ISO 20022 adoption progresses.
List of ISO 20022-compliant cryptocurrencies
A crypto that complies with the ISO 20022 standard could be approved by a centralized bank that enables crypto payments. ISO-standardized crypto identifiers are going to change the way crypto is used. If ISO issues an official code for crypto, such as Bitcoin or Ether (ETH), that crypto will enter the database tables of top financial services like Visa and MasterCard.
For cryptos to be classified as legitimate currencies by ISO, they must comply with new standards in global financial systems and have an ISO code that doesn’t conflict with existing codes.
These nine (9) coins and tokens have been certified as ISO 20022-compliant:
Quant ($QNT)
Quant ($QNT) is a blockchain project aiming to revolutionize how multiple blockchains and traditional financial systems interoperate. At its core, Quant seeks to address the issue of interoperability, which refers to the seamless communication and collaboration between different blockchain networks and legacy financial systems.
The project introduces Overledger, a platform designed to serve as a universal connector that enables cross-chain transactions, data sharing, and the development of decentralized applications (dApps) that can operate across multiple blockchains. Overledger’s unique technology allows it to interact with various distributed ledger technologies, making it possible for disparate blockchains to communicate and exchange value securely and efficiently. This interoperability could enhance the blockchain ecosystem’s overall scalability, liquidity, and functionality, fostering a more interconnected and versatile decentralized landscape.
The $QNT token plays a crucial role within the Quant ecosystem. As the native utility token, $QNT is used to pay transaction fees, access services on the Overledger platform, and incentivize network participants to maintain and secure the network. The token’s supply is fixed, which adds a deflationary aspect to its value proposition. The successful implementation of Quant’s technology could pave the way for greater collaboration between various blockchain networks and establish a bridge between blockchain and traditional financial systems. By addressing the interoperability challenge, Quant aims to unlock new opportunities for innovation, streamline cross-border transactions, and ultimately contribute to the broader adoption of blockchain technology in diverse industries.
Ripple ($XRP)
Ripple ($XRP) is a cryptocurrency and a digital payment protocol that aims to transform the way global financial transactions are conducted. Unlike traditional blockchain systems that rely on proof-of-work or proof-of-stake mechanisms, Ripple utilizes a unique consensus algorithm called the Ripple Protocol Consensus Algorithm (RPCA). This algorithm facilitates fast and efficient transactions by validating and reaching consensus across a network of trusted nodes without energy-intensive mining processes. Ripple’s primary focus is enabling real-time, cross-border payments and remittances for financial institutions and banks, offering them a cost-effective alternative to the traditional Swift network. The $XRP cryptocurrency is a bridge currency within the Ripple network, facilitating the seamless value exchange between different fiat currencies.
One of Ripple’s notable products is RippleNet, a global payment network that connects banks and payment providers to facilitate secure and near-instantaneous cross-border transactions. Ripple’s technology, including its Interledger Protocol (ILP), aims to reduce settlement times and significantly lower transaction costs, enhancing financial institutions’ transparency and liquidity management.
The company’s partnerships with various major players in the financial industry have helped propel its solutions to the forefront of blockchain-based financial innovation. However, Ripple has also faced regulatory challenges related to the classification of $XRP as a security by some authorities, which has led to legal disputes and fluctuations in the cryptocurrency’s value. Despite these challenges, Ripple’s focus on revolutionizing cross-border payments remains a significant driver of its ongoing development and adoption efforts.
Stellar ($XLM)
Stellar ($XLM) is a cryptocurrency and a decentralized payment platform designed to facilitate fast, low-cost cross-border transactions and enable financial inclusion for individuals and businesses worldwide. Developed as a fork of the Ripple protocol, Stellar aims to create a global network that connects financial institutions, payment processors, and individual users, making it easier to move money across borders and provide access to essential financial services. The Stellar platform utilizes its consensus algorithm called the Stellar Consensus Protocol (SCP), allowing quick transaction confirmation by a network of trusted nodes without resource-intensive mining.
At the core of the Stellar network is the Lumens ($XLM) cryptocurrency, which serves as a bridge asset that enables the seamless exchange of value between different currencies and facilitates cross-border transactions. Lumens also play a vital role in preventing spam attacks and ensuring the security and reliability of the Stellar network.
Beyond its payment capabilities, Stellar strongly focuses on supporting micropayments and enabling the issuance of digital assets through its decentralized exchange capabilities. This feature makes it well-suited for applications such as remittances and tokenized assets, as well as facilitating access to financial services in regions lacking traditional banking infrastructure. Stellar’s open and inclusive approach to connecting financial systems aligns with its mission to create a more inclusive and accessible global financial ecosystem.
Hedera ($HBAR)
Hedera Hashgraph ($HBAR) is a decentralized public network that utilizes a novel algorithm known as the Hashgraph consensus to achieve high scalability, security, and fairness levels. The platform aims to provide a foundation for creating and deploying decentralized applications (dApps) and services across various industries, from finance and supply chain management to gaming and social networking. Unlike traditional blockchains, Hedera Hashgraph employs a directed acyclic graph ($DAG) structure to enable fast and efficient consensus among network participants, resulting in rapid transaction speeds and minimal energy consumption.
The $HBAR cryptocurrency is the native digital asset of the Hedera network and serves multiple purposes within the ecosystem. It is used to pay for transaction fees, secure the network through staking, and participate in the consensus process. $HBAR’s fixed supply and deflationary mechanisms contribute to its value proposition. Hedera also emphasizes security and governance by employing a council of trusted enterprises from various industries, which play a role in decision-making and network management. This unique approach balances decentralization and practicality, making Hedera Hashgraph an exciting option for organizations seeking a scalable and secure decentralized application and service platform.
$IOTA (MIOTA)
$IOTA (MIOTA) is a unique cryptocurrency and distributed ledger technology focusing on the Internet of Things (IoT) ecosystem. Unlike traditional blockchain systems, $IOTA utilizes a directed acyclic graph ($DAG) structure called the Tangle, designed to handle microtransactions and data transfers between IoT devices in a scalable and feeless manner. The Tangle’s structure allows each new transaction to confirm two previous transactions, creating a more efficient and secure network as more transactions are added. This innovation makes $IOTA particularly suited for enabling machine-to-machine communication and microtransactions within the IoT landscape.
The MIOTA token is the native digital currency of the $IOTA network and is used to facilitate transactions and data transfers within the Tangle. Its feeless nature removes barriers to small-value transactions, making it well-suited for microtransactions in IoT scenarios. $IOTA’s focus on scalability, security, and seamless transactions aligns with its vision of becoming a foundational technology for the rapidly growing Internet of Things industry. However, $IOTA has also faced technical challenges and criticisms, including concerns about centralizing its Coordinator node, which has been necessary for network security. The project is actively working on addressing these issues. It continues evolving as a potential disruption in the IoT space, offering a novel approach to decentralized data and value exchange.
$XDC Network ($XDC)
$XDC Network ($XDC) is a blockchain platform facilitating secure and efficient cross-border transactions, trade finance, and supply chain management. Built upon the XinFin Hybrid Blockchain, $XDC Network combines the benefits of both public and private blockchains to create a scalable and interoperable ecosystem. One of its primary focuses is bridging the gap between traditional finance and blockchain technology by offering a platform that can streamline global trade processes and reduce inefficiencies in the supply chain. $XDC Network’s consensus mechanism, XDPoS (XinFin Delegated Proof of Stake), ensures fast transaction confirmations while maintaining network security and decentralization.
The $XDC token is the native digital asset of the $XDC Network. It serves as a utility token to pay for transactions, access various services within the platform, and participate in network governance. $XDC’s focus on real-world use cases, especially in trade finance and supply chain management, sets it apart as a blockchain solution targeting tangible and practical applications. $XDC Network aims to address global trade and finance challenges through its interoperability and integration capabilities, making cross-border transactions more efficient, transparent, and accessible for businesses and individuals.
Algorand ($ALGO)
Algorand ($ALGO) is a blockchain platform that provides a highly scalable, secure, and decentralized environment for building decentralized applications (dApps) and facilitating efficient blockchain transactions. One of Algorand’s key innovations is its proprietary consensus mechanism, Pure Proof of Stake (PPoS), which enables fast transaction confirmation times while maintaining a high level of decentralization. Unlike traditional proof-of-work systems, Algorand’s PPoS ensures that all participants have an equal opportunity to propose and validate new blocks, enhancing the network’s security and eliminating the need for resource-intensive mining.
The $ALGO token is the native cryptocurrency of the Algorand network, serving as both a medium of exchange and a means to participate in the network’s consensus process. $ALGO holders can actively participate in block validation and earn rewards for their contributions. Algorand’s focus on scalability, low transaction fees, and rapid confirmation times makes it suitable for various applications, including financial services, decentralized finance (DeFi), and asset tokenization. The platform’s commitment to delivering a secure and efficient blockchain infrastructure has positioned Algorand as a contender in the competitive blockchain space, aiming to address the challenges of scalability and transaction speed while fostering innovation in the decentralized ecosystem.
Cardano ($ADA)
Cardano ($ADA) is a blockchain platform that aims to provide a secure and scalable infrastructure for developing decentralized applications (dApps) and smart contracts. Developed through a rigorous research-driven approach, Cardano focuses on scalability, sustainability, and interoperability to address the limitations of existing blockchain technologies. The platform is divided into two layers: the Cardano Settlement Layer (CSL) for handling cryptocurrency transactions and the Cardano Computation Layer (CCL) for executing smart contracts. Cardano utilizes a proof-of-stake consensus algorithm called Ouroboros, which ensures network security and energy efficiency by allowing participants to earn rewards through staking their $ADA tokens.
$ADA is the native cryptocurrency of the Cardano network and serves various purposes within the ecosystem. It can be used for transactions, staking, and participating in platform governance through voting on proposals and upgrades. Cardano aims to enhance blockchain scalability through its layered architecture, fostering innovation and adoption in finance, identity management, and supply chain sectors. Additionally, Cardano strongly focuses on peer-reviewed research and academic collaboration, seeking to combine theoretical rigor with practical implementation to offer a robust and future-proof blockchain platform.
Verge ($XVG)
Verge ($XVG) is a privacy-focused cryptocurrency that strongly emphasizes user anonymity and transaction confidentiality. It utilizes a variety of privacy protocols, including Tor (The Onion Router) and I2P (Invisible Internet Project), to obfuscate transaction data and IP addresses, providing users with enhanced privacy and security. Verge’s primary goal is to offer a decentralized and private digital currency that enables individuals to conduct transactions without revealing their identities or transaction details to the public.
Each of these coins was developed to make global transactions more accessible, which allowed them to comply more quickly with the ISO 20022 standard.
However, this list will only expand as more cryptos get included in the worldwide payment sector and move toward ISO 20022 compliance.
And just because they follow ISO 20022 doesn’t necessarily mean they’re suitable investments.
Ripple is an excellent example of crypto with numerous disadvantages compared to benefits – and Helena Margarido encourages you to avoid it. (Here’s why.)
Hedera is a fascinating penny coin with a lot of potential that you can learn more about here, and it certainly belongs on your watchlist. (These picks were hand-chosen by our team of experts if you’re searching for penny coins that are flashing buys.)
Verge ($XVG)Token, the latest ISO 20022 -Compliant Asset
Verge unveiled a significant milestone in cryptocurrencies on June 5th: its native token, $XVG, is now fully ISO 20022-compliant. This development marks a turning point for Verge, positioning its digital currency to gain a competitive advantage and accelerate the widespread adoption of $XVG.
Verge’s achievement is groundbreaking within the crypto realm and the broader landscape of digital currencies. It solidifies Verge’s position as the 9th cryptocurrency to adopt the ISO 20022 standard. However, what sets Verge apart is that it is the pioneering decentralized Internet of Things (IoT) community-run currency to achieve ISO 20022 compliance.
Collaborative efforts with partners Voice Life and BlockDudes played a pivotal role in this accomplishment. Voice Life’s involvement introduced a novel concept: the distribution of passive income for Fractional Non-Fungible tokens (F-NFT) holders through the $XVG coin. BlockDudes, however, has been the driving force behind the meticulous implementation process, ensuring a seamless transition.
This milestone follows Verge’s distinction as not being categorized as a security, a monumental leap forward for cryptocurrency. Verge’s mission as an open-source, community-driven digital currency revolves around bridging the divide between the crypto sphere and traditional financial systems.
Verge remains resolute in upholding the core tenets of public ledger currencies, echoing the principles set forth by the enigmatic Satoshi Nakamoto, the creator of Bitcoin.
ISO 20022 standards were not initially tailored for the intricacies of cryptocurrencies, making $XVG’s compliance even more remarkable. This decision is poised to broaden $XVG’s horizons and amplify its presence within the global financial landscape. The announcement portrays this achievement as a defining moment in Verge’s evolutionary journey, setting the stage for the future of digital currencies.
How is ISO 20022 changing in 2024?
The ISO 20022 financial messaging standard, used for high-value and international payments, will undergo significant transformations in 2024.
A notable change is the implementation of the Swift Transaction Manager (TM), which will progressively enhance data integrity rules. New rules for bypass and aborts are slated for introduction in 2024 and 2025.
Moreover, corporate readiness for ISO 20022 is anticipated to reach a crucial stage by 2024. For instance, the Bank of England plans to transition its Real-Time Gross Settlement System and high-value payment messages to ISO 20022 in the summer of 2024.
These modifications are part of a larger shift towards a complete industry transition to ISO 20022, expected to conclude by November 2025. This transition aims to adopt a universally shared language that offers valuable enhanced data.
SWIFT implementation of the standard
The coexistence of SWIFT and ISO 20022 for cross-border payments and reporting (CBPR+) began on March 20, 2023, initiating a significant phase in the global payments industry. During the coexistence period, extending until November 2025, SWIFT will support MT (Message Type) and ISO 20022, allowing financial institutions to migrate to the new standard at their preferred pace.
This development represents an essential milestone in adopting ISO 20022, as it allows for a smooth transition period and accommodates the varying readiness of different institutions. SWIFT, the global provider of secure financial messaging services, will offer continued support throughout this coexistence phase, facilitating the integration of ISO 20022 and its structured data within the financial community.
Furthermore, SWIFT actively assists real-time gross settlement systems (RTGSs) in implementing ISO 20022 for domestic payments. Several major market infrastructures, such as Australia’s RITS, Canada’s LYNX, Europe’s EURO 1 and T2, and New Zealand’s ESAS, migrated to ISO 20022 on March 20, 2023. Other RTGSs worldwide are also preparing to adopt the standard and will go live in the coming months and years.
Adopting the standard by SWIFT and RTGSs allows for greater harmonization and standardization in cross-border and domestic payment systems. It introduces structured data, offering enhanced transparency, improved processing efficiency, and better analytics capabilities. Ultimately, the successful coexistence of SWIFT and ISO 20022 paves the way for enhanced cross-border payment experiences and opens up new possibilities for the global payments industry.
How will ISO 20022 implementation impact different players in the industry?
Implementing ISO 20022 within the financial sector can substantially affect stakeholders, including financial institutions, corporations, market infrastructures, and technology providers. These impacts can be advantageous and demanding, contingent upon specific circumstances and each participant’s readiness. Here’s a breakdown of how different industry players may be influenced:
- Financial Entities (Banks, Payment Service Providers, etc.):
Operational Streamlining: ISO 20022 can bolster operational efficiency by offering a uniform messaging format, diminishing manual intervention and transaction errors.
Data Enhancement: Financial entities gain access to more extensive and well-structured data, which bolsters risk management, fraud detection, and customer service.
Compliance and Regulatory Implications: Regulatory authorities may mandate ISO 20022 compliance for particular transaction categories, necessitating system enhancements and internal process adjustments.
Cost Considerations: Implementing ISO 20022 may incur significant expenses, including system upgrades, workforce training, and data migration.
- Business Entities (Companies and Corporations):
Efficient Transaction Processing: ISO 20022 allows business entities to achieve higher straight-through processing rates (STP), curtailing manual effort and transaction inaccuracies.
Enhanced Visibility: The enriched data in ISO 20022 messages furnishes businesses with more comprehensive insights into their financial transactions, enabling advanced cash management and treasury operations.
Integration Challenges: Businesses may need to adapt their internal systems and processes to align with ISO 20022, necessitating investments in technology and workforce training.
- Market Infrastructure Providers (Stock Exchanges, Clearinghouses, Payment Systems):
Promotion of Interoperability: ISO 20022 promotes interoperability among market infrastructures and payment systems, streamlining cross-border and cross-system transactions.
Risk Management Improvements: The standardized format bolsters market infrastructure risk management and surveillance capabilities.
Migration Complexities: Market infrastructure providers may confront intricate migration initiatives when transitioning from legacy messaging formats to ISO 20022.
- Technology Solution Providers (Software and Service Providers):
Business Opportunities: Technology providers can offer tailor-made solutions and services to aid financial institutions and other participants in their ISO 20022 adoptions.
Fostering Innovation: ISO 20022 can stimulate innovation in financial technology by enabling the development of applications and services that harness the standardized data.
- Regulatory Authorities:
Enhanced Supervision: Regulatory bodies can benefit from enhanced visibility into financial transactions, augmenting their capacity to oversee and regulate the financial sector.
Advocacy for Standardization: Regulatory authorities can advocate for standardization and transparency within the financial industry by mandating the adoption of ISO 20022 for specific transaction categories.
The impact of ISO 20022 implementation hinges on the preparedness and adaptability of each participant within the financial industry. While it offers myriad advantages in terms of efficiency and data richness, the transition can be demanding, necessitating technological investments and business process alterations. Effective incorporation of ISO 20022 positions organizations to better address the financial landscape’s evolving demands and regulatory requisites.
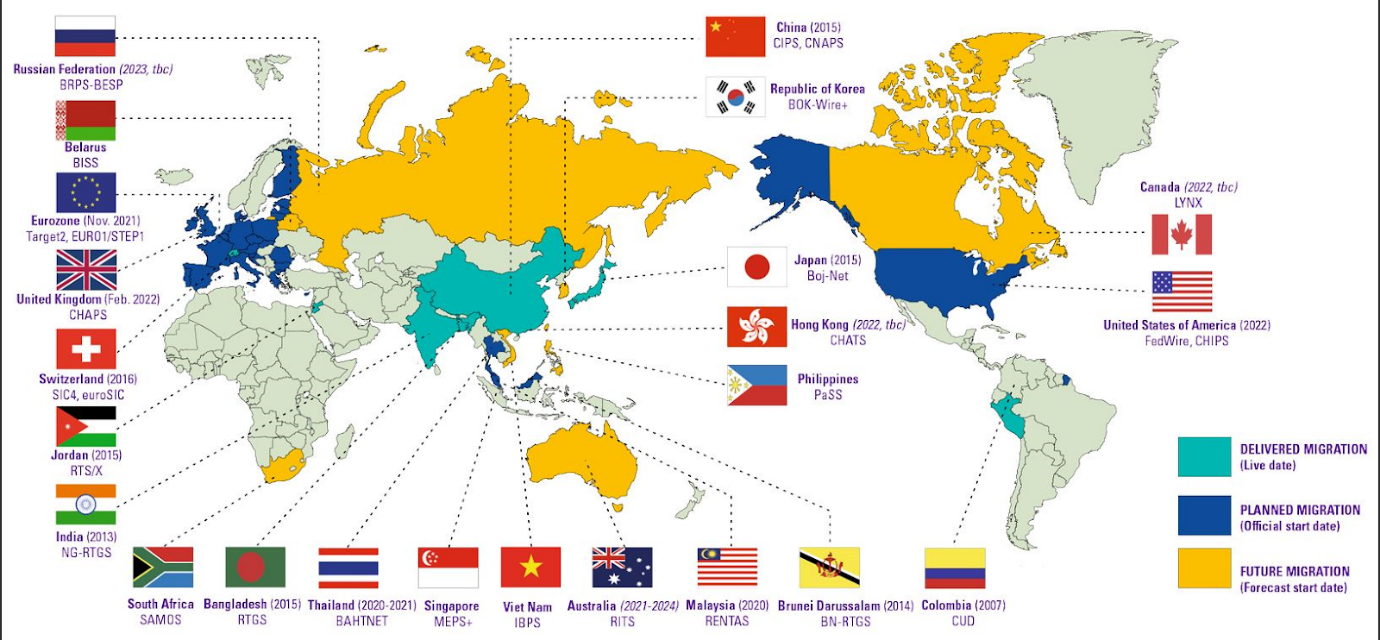
What impact will ISO 20022 have around the world?
The ISO 20022 standard will completely change the financial landscape and improve international money transfers. Europe transitioned to ISO 20022 towards the end of 2022, and the US implemented it in 2023.
Cryptos that update their systems to comply with this new ISO standard will likely appreciate if they are chosen for payments by banks.
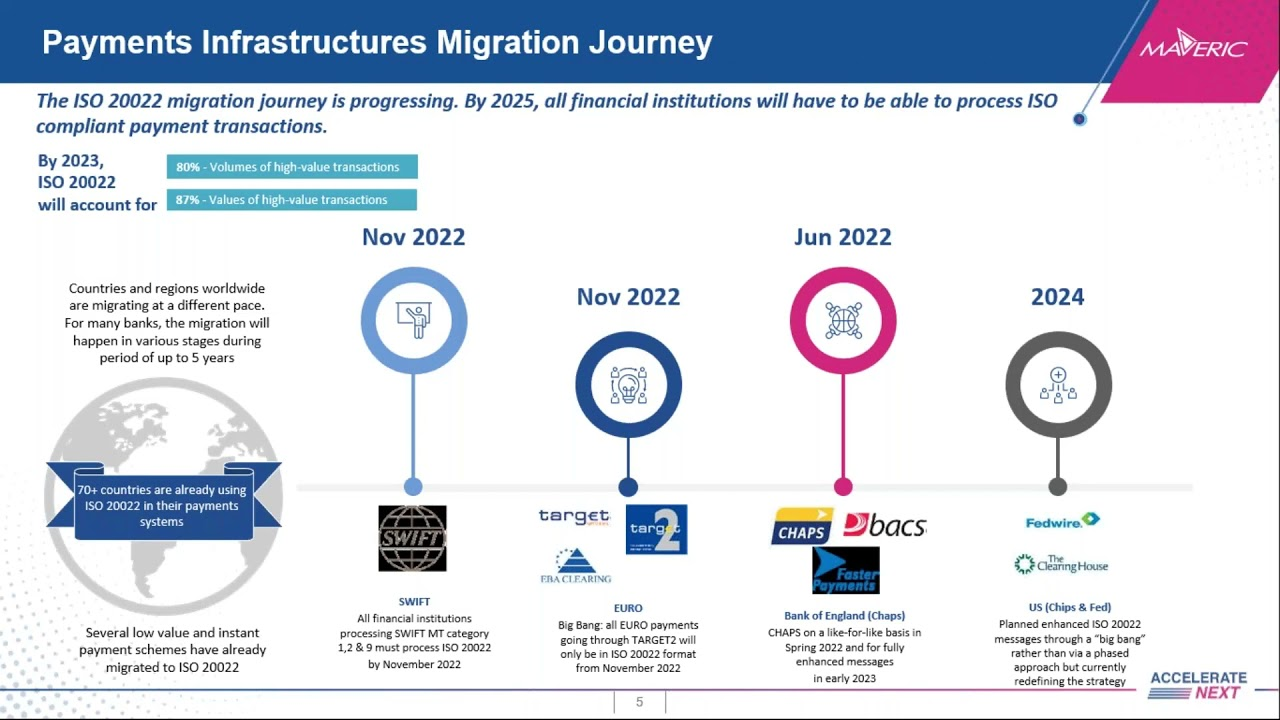
Over 70 countries, including Switzerland, China, India, and Japan, have adopted ISO 20022 in their payment systems. With over 200 payment types in scope, it will harmonize formats and data components from different payment methods that could not previously work together.
The ISO standard will apply to domestic, real-time, high-value, and cross-border payments.
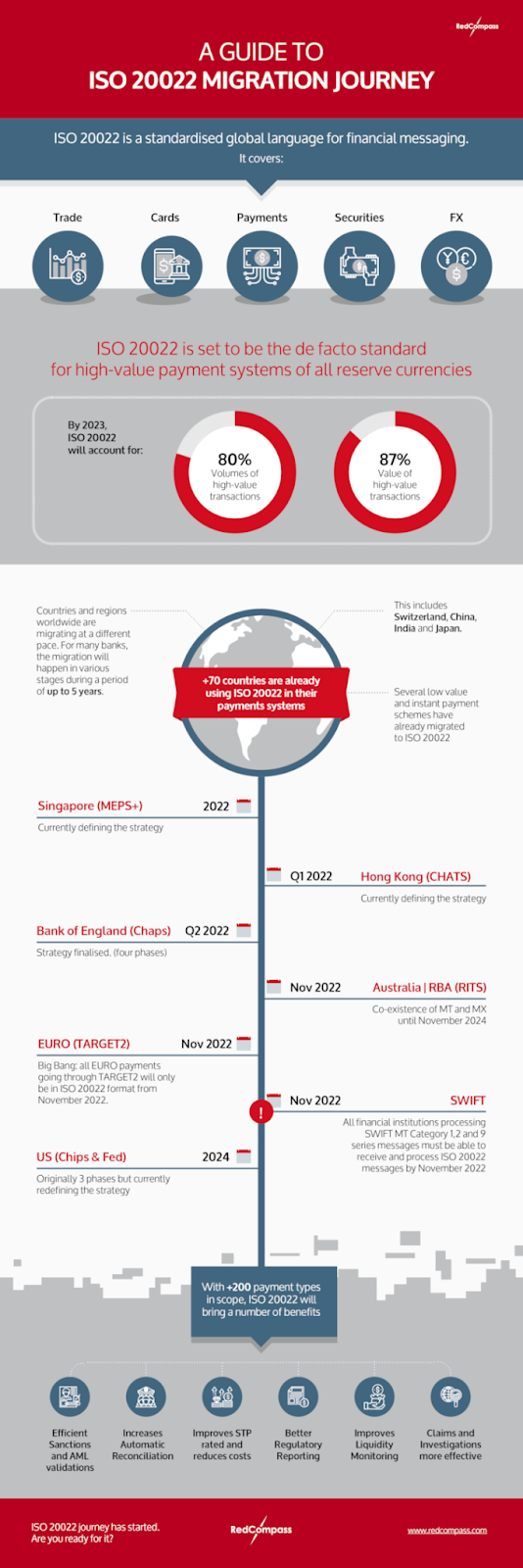
What banks must do to stay ahead of the competition
SWIFT’s technological shift from MT to ISO 20022 will be complete. Banks must upgrade their messaging interfaces and test them before November 2022 to ensure they are compatible with the new payment communication standard.
Banks are under competitive strain to migrate to this new standard as the overall migration of the payment industry toward immediate payments makes their existing goods and services vulnerable.
Because this standard is a more modernized and versatile standard than conventional legacy formats, it requires significantly greater data volume processing. As a result, bank systems and databases will need to be capable of handling these larger volumes at quicker speeds for real-time payments, daily liquidity management, compliance checks, and fraud detection and prevention.
It’s critical to allow enough time for testing so that syntax and formatting information is accurate, and the data’s migration into all linked payment and clearing systems. Testing should ideally be completed by the second quarter of 2022 at the latest.
Banks must inform their corporate customers about the additional data that may be accessible and how it will be utilized. In addition, those clients should be completely informed and involved in end-to-end testing.
Below is the timeline for ISO 20022 migration.
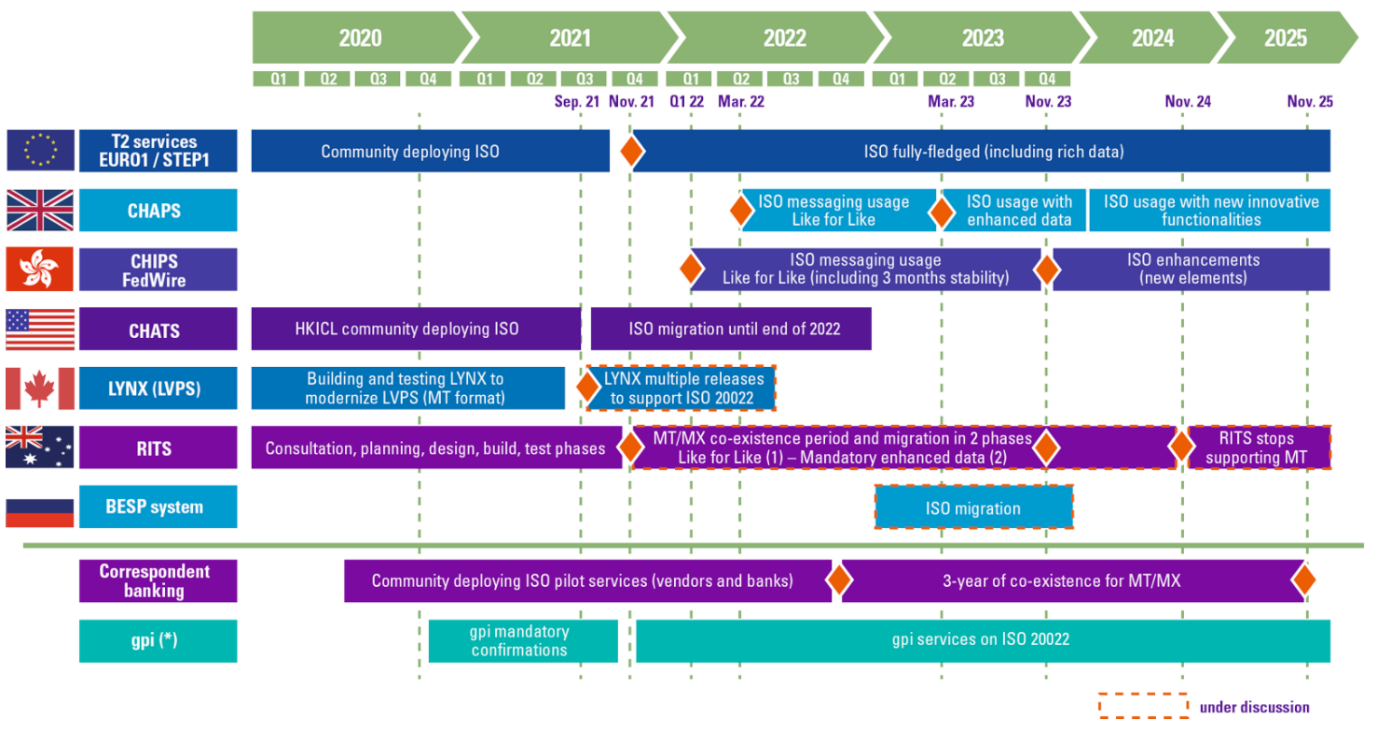
High-Value Payments (HVPs) on ISO 20022
To establish a road map to standardization for high-value payments and real-time gross settlement (RTGS), the SWIFT, global central banks and market infrastructures have established the HVPS+ market practice task group.
“By unifying messaging standards across HPVs, participants in the payment system will be able to benefit from efficiencies and lay the groundwork for new services.” Michael Knorr, Wells Fargo Bank’s Head of Payments & Liquidity Management for Financial Institutions.
To stay on top of these high-value payment systems, you’ll need a solution to keep track of them. HVP systems are crucial to international finance, so monitoring these significant value transfers with the appropriate monitoring and performance management solution is critical.
RTGS is changing the global financial landscape
Challenges of ISO 20022
Implementing the standard can present several challenges for financial institutions. Here are some of the critical challenges associated with ISO 20022 implementation:
- Standard complexity: It is a comprehensive standard with rules and specifications. Financial institutions must understand the intricacies of ISO 20022 as a new business standard and ensure compliance with the required rules, including those related to anti-money laundering (AML), fraud, and compliance checks.
- Addressing differences in market infrastructures: While various payment schemes may adopt the standard, there can be differences in the implementation guidelines for different market infrastructures. Financial institutions must navigate and address these variations to ensure interoperability and compliance across different payment systems.
- Upgrading legacy systems: Many financial institutions still rely on legacy systems that may not be capable of processing or supporting the new format. Upgrading or replacing these aging systems is often necessary to leverage the opportunities presented by ISO 20022. This process involves significant budgeting and coordination with stakeholders and partners.
- Establishing the right migration timeline: Its adoption deadlines vary across different markets and jurisdictions. Financial institutions operating across borders must carefully plan their migration strategy, considering their organizations’ diverse deadlines and potential complexities.
- Managing the pressure to change: Migration is just one of the transformation projects financial institutions may undertake simultaneously. Combined with regulatory deadlines, there can be intense pressure to implement changes quickly. However, rushed implementations may result in suboptimal solutions. Financial institutions must balance the need for timely compliance with the long-term strategic goals of their organization.
- Implementing new data management: Its messages can be more extensive than previous messaging formats, potentially resulting in a significant increase in data volume. In the standards, every character in a financial message must be 100% correct and adhere to the prescribed format. The validation process occurs at various stages along the communication channel, both on the sending and receiving ends. Even a minor error, such as a missing colon, can have significant consequences.
A strong migration plan should exhibit the following characteristics to address these challenges:
- Clearly-defined long-term strategy: The migration plan should align with the organization’s long-term goals and objectives, considering the potential benefits and opportunities that it can offer.
- Comprehensive impact analysis: Financial institutions should conduct a thorough assessment of the impact of ISO 20022 implementation on their systems, processes, and stakeholders. This analysis will help identify potential risks and challenges that need to be addressed.
- Robust and systematic project management: Effective project management is crucial for successfully implementing ISO 20022. Financial institutions should establish clear governance structures, allocate appropriate resources, and follow a structured approach to manage migration.
- Effective internal communications: Communication is key throughout the ISO 20022 implementation process. Financial institutions must ensure that all relevant stakeholders, including internal teams, external partners, and clients, are well-informed about the migration plan, its timeline, and its expected impact on their operations.
- Future-proof technology and testing solution: To ensure a smooth transition, financial institutions should invest in technology solutions that support ISO 20022 messaging and offer scalability, flexibility, and compatibility with future developments. Rigorous testing is essential to verify the interoperability and functionality of systems before and after migration.
CON: ISO 20022 Compliance is Antithetical
The foundational ethos of cryptocurrency was to forge a path distinct from traditional banks and the overarching financial sector. Rooted in the aftermath of the late 2000s financial turmoil, Bitcoin emerged as the progenitor of this new digital currency landscape.
The public sought an alternative in the form of peer-to-peer electronic cash systems with efficient transaction capabilities — a service also provided by banks and touted as a major advantage. Yet, for many, the drawbacks of centralized banking outweighed the benefits.
Cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin were thus innovated to offer peer-to-peer transactional functionality independent of central banks and their authoritative regulations. The core of this innovation was self-governance and decentralization.
In this light, integrating ISO 20022 standards seems contradictory, steering away from the original vision of cryptocurrencies. By aligning with a global standard, the fundamental philosophy of the cryptocurrency movement risks being compromised despite any claims of neutrality from the standards organization.
The New Quantum Financial System (QFS) and Its Alignment with ISO 20022
The New Quantum Financial System (QFS) is a theoretical global monetary system leveraging quantum computing, quantum-secure blockchain encryption, and quantum cryptography.
The QFS finds a natural ally in ISO 20022 for several compelling reasons:
- Seamless Standardization: Integrating ISO 20022 within the QFS framework is essential for ensuring compatibility with existing and future financial networks. This standardization is a cornerstone for the QFS, enabling it to integrate smoothly with the global financial infrastructure.
- Rich Data for Advanced Processing: The detailed and structured nature of ISO 20022’s data format complements the sophisticated data processing capabilities of the QFS. This feature enhances accuracy and depth in financial analytics and decision-making processes.
- Expanding Global Footprint: ISO 20022 adoption is growing across international financial systems, and its incorporation into the QFS significantly broadens the system’s global interoperability. This integration is crucial for the QFS to function effectively across diverse financial landscapes worldwide.
- Adaptability for the Future: The flexible and extensible nature of ISO 20022 makes it well-suited for evolving technological landscapes. For a forward-thinking system like the QFS, adopting a standard that can adapt to future changes is vital for maintaining long-term operational efficiency and relevance.
The Combined Impact on Future Finance
The fusion of ISO 20022 with the Quantum Financial System represents more than technical compatibility; it signals a strategic move towards a unified, efficient, and transparent global financial ecosystem. As we progress towards a future where digitalization and advanced technologies become increasingly prevalent, the collaboration between QFS and ISO 20022 is poised to be instrumental in shaping a streamlined and sophisticated landscape for financial transactions and communications.
Conclusion
The ISO 20022 was developed by the “Registration Management Group,” which comprises 37 of the world’s largest financial players, including Ripple ($XRP). Ripple’s vice president claims that Ripple already complies with ISO 20022 and, together with RippleNet, will be the first crypto company ready for the new global financial standard.
The ISO 20022 protocol will revolutionize the way we make payments. With its secure and reliable features, it will help financial institutions around the world improve efficiency and reduce fraud. As implementation began in 2023, different players in the industry must start preparing for a seamless transition to take advantage of the potential benefits of this new protocol. With the ability to process data-rich payments, the ISO 20022 protocol will revolutionize the payment industry worldwide.
Keeping up with new technologies, legal changes, and the introduction of new international payment standards is difficult. With ISO migration just around the corner, organizations can turn data into knowledge to ensure worldwide payment systems run safely and effectively.
In 2025, ISO will be the global standard for high- or large-value payment systems in all reserve currencies and is projected to handle 80% of all transactions, including 87% of transaction value globally. The European Central Bank and SWIFT have announced the ISO 20022 go-live dates for the standard.
 cryptopolitan.com
cryptopolitan.com
