After a turbulent 2023 followed by a recovery in 2024, the global count of crypto-automated teller machines (ATMs) is inching closer to its former high of 39,958, achieved on Dec. 1, 2022.
Crypto ATMs Prove Resilient in Post-Terra and FTX Era, Near Record Numbers
The trajectory of crypto ATMs saw dramatic shifts following the Terra stablecoin crisis and the FTX collapse in Nov. 2022. According to coinatmradar.com, the worldwide count of crypto ATMs hit its zenith of 39,958 by Dec. 1 of that year.
Presently, the total number of these machines is only 1,092 shy of that peak. This marks a significant departure from the declines witnessed in April and July 2023. Following the all-time high, the number of machines experienced a reduction of 6,873, reaching a low of 33,085 on July 1, 2023.
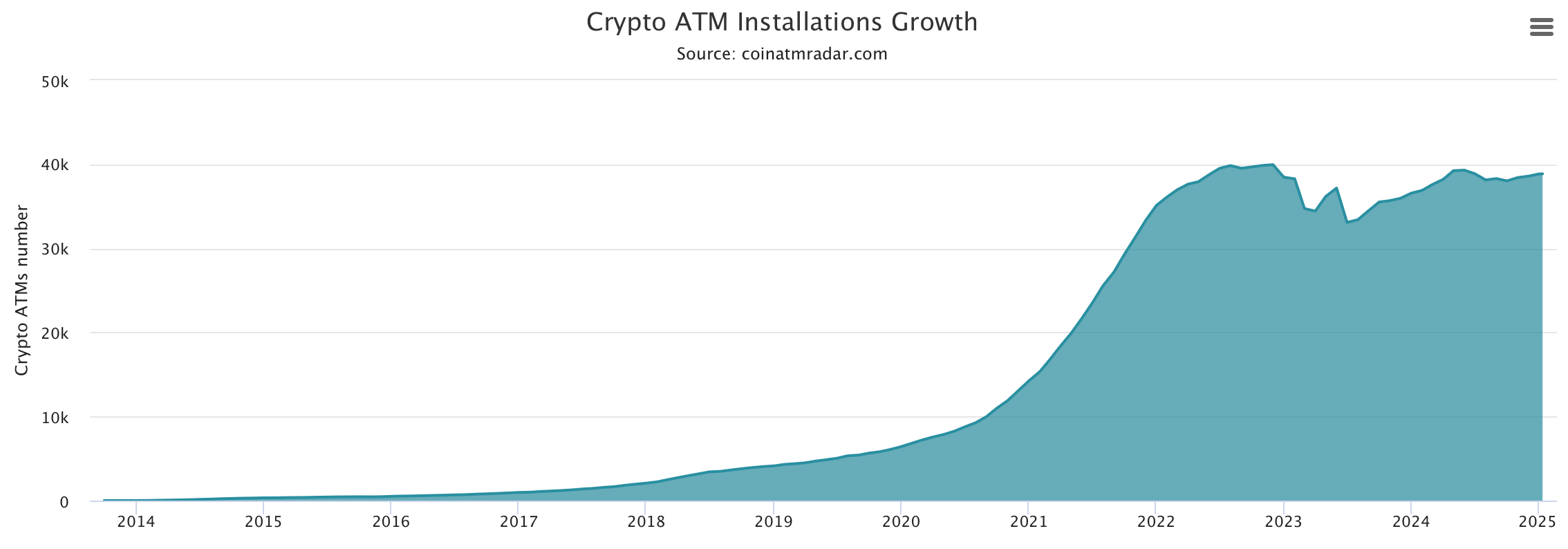
Coinatmradar.com data indicates that, as of Jan. 11, 2025, there are 38,866 crypto ATMs in operation globally. Of those, 283 machines have been installed since the beginning of this year, with 157 added in December alone. November brought a net increase of 404 devices, while October 2024 saw a decline of 280.
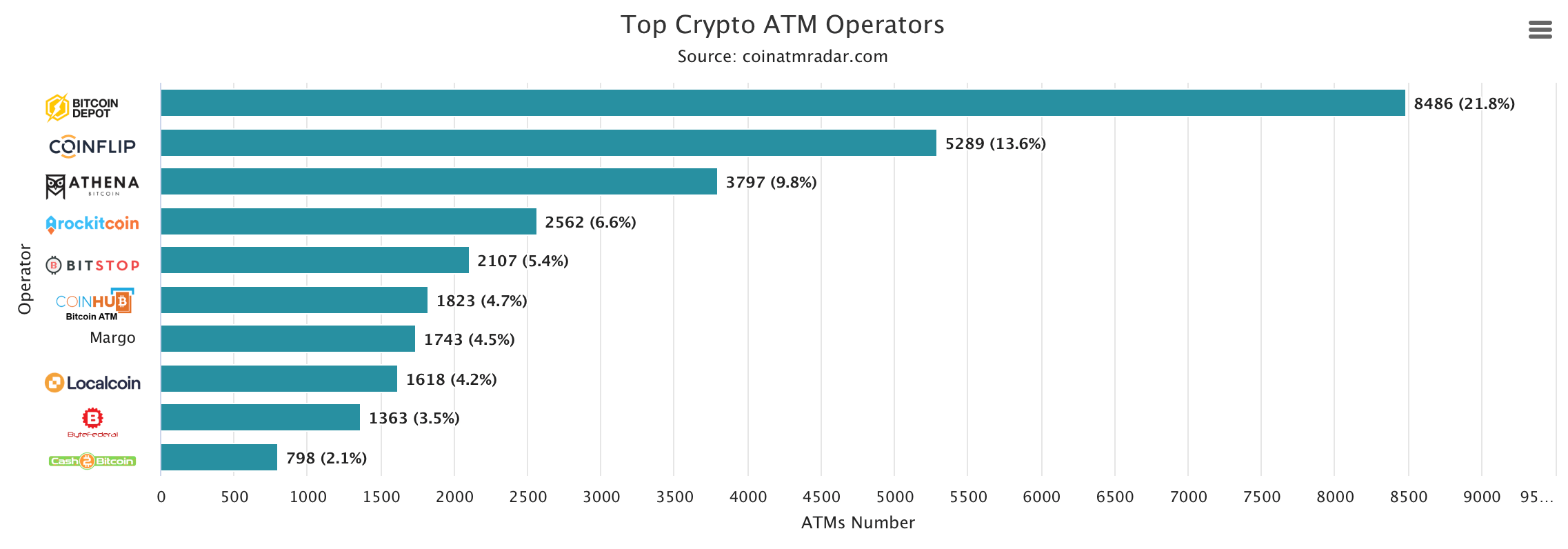
Bitcoin Depot holds the title of the largest operator by machine count, managing 8,486 ATMs worldwide as of Jan. 11, 2025, according to coinatmradar.com stats. Coinflip follows with 5,289 machines, while Athena Bitcoin oversees 3,797 devices.
Geographic data from coinatmradar.com shows the United States dominates this space, hosting 81.3% of all crypto ATMs worldwide. On a regional level, Europe accounts for 4.3% of the machines, Oceania claims 4% and 3.5% are stationed in Australia.
Of the 38,866 devices, a vast majority—38,855—support bitcoin (BTC). Among alternative coins, litecoin (LTC) is the most widely supported, appearing on 54.2% of machines, followed by ethereum (ETH) at 53.3% and dogecoin (DOGE), which is available on 10,767 ATMs or 27.7% globally.
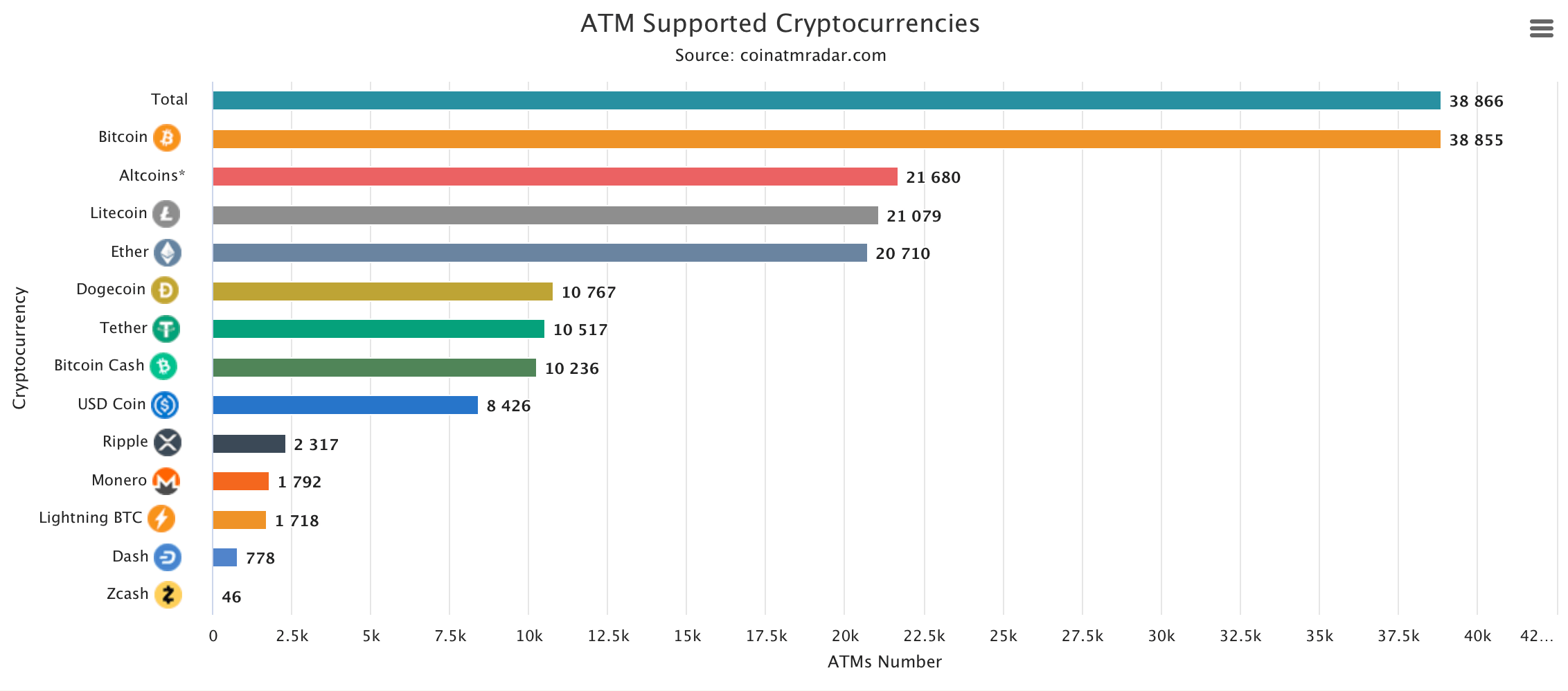
The global proliferation of crypto ATMs captures a compelling blend of innovation and resilience within the constantly shifting cryptocurrency sphere. As installation trends wax and wane in response to market forces, these machines serve as concrete bridges linking digital currencies to physical access points.
Their evolving distribution reflects an enduring demand for decentralized financial (defi) tools in a tangible world, shaping the future of monetary engagement.
 news.bitcoin.com
news.bitcoin.com
