Bitcoin has taken the world by storm in the last decade, going from an obscure invention to an asset with a market capitalization measured in the hundreds of billions of dollars. However, the technology is still relatively new and there’s a lot of misconceptions about Bitcoin among newcomers.
It’s very common for newcomers to crypto to wonder what does a Bitcoin look like. In this article, we’ll explain why this question doesn’t have a good answer and hopefully help you understand how Bitcoin works on a conceptual level.
What does a Bitcoin look like?
Bitcoin is an entirely digital asset, so it doesn’t really have a “look”. At its very core, Bitcoin is binary code consisting of 0s and 1s that represents data and specifies operations to be performed by a processor.
However, members of the Bitcoin community often represent Bitcoin as a gold-colored coin engraved with the Bitcoin symbol in the middle and various writing, typically about Bitcoin’s decentralized and peer-to-peer properties, around the edge.
Such physical representations of Bitcoin are sometimes sold as souvenirs or gifts, but they don’t have any value other than the metal they’re made out of.

Example of a physical representation of Bitcoin. Such “Bitcoins” don’t represent any actual $BTC coins.
The Bitcoin Core client, which is the reference implementation of Bitcoin, is written in the C++ programming language. Since it’s entirely open source, you can see what the Bitcoin Core code looks like on the project’s GitHub page. However, other Bitcoin clients might use other programming languages — the important thing is that the client adheres to the set of rules known as the Bitcoin protocol.

Example of C++ code from the Bitcoin Core implementation of Bitcoin.
In the digital realm, $BTC coins exist as unspent transaction outputs (UTXOs). UTXOs must be spent in full.
For example, if you have a 1 $BTC UTXO and want to send 0.1 $BTC to someone, what will actually happen is that the full 1 $BTC will be sent and you will receive back a new UTXO worth 0.9 $BTC (minus transaction fees). Conceptually, this system works similar to cash — if you use a $10 bill to pay for an item priced at $1, you’d get $9 back.
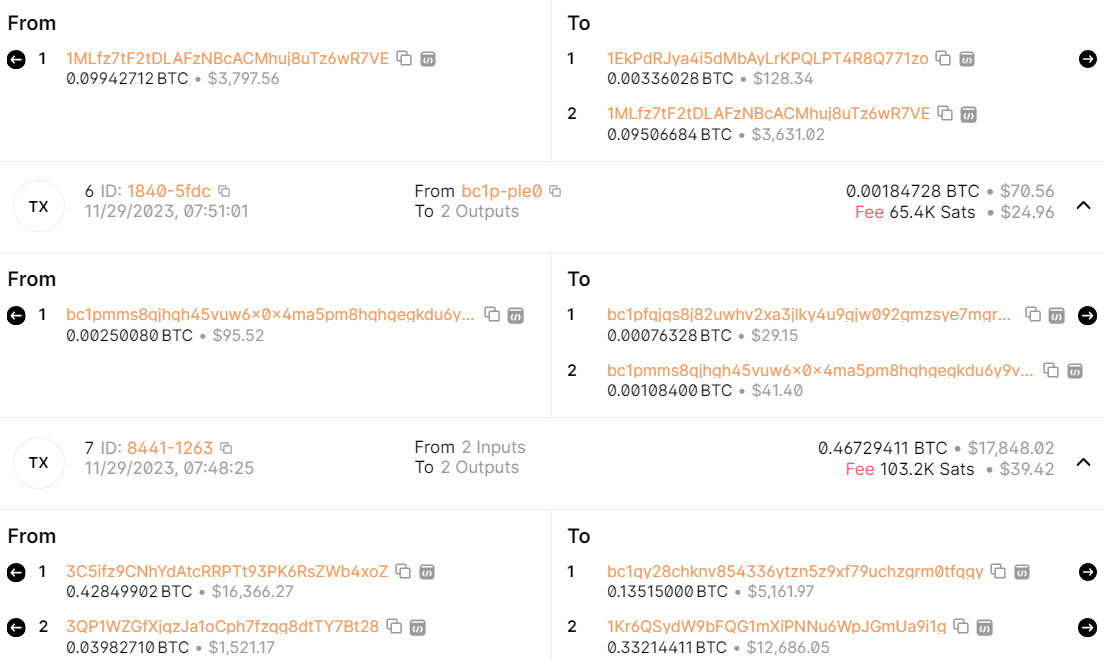
Looking at Bitcoin transaction details using a block explorer.
Unless you’re an advanced user with very specific requirements, you don’t need to worry about the UTXO model when sending a Bitcoin transaction with your wallet, as everything is handled automatically.
“Physical” Bitcoins
Some people enjoy having their valuable possessions represented a tangible form. Over the years, we have seen several “physical Bitcoin” products that are tangible items with an associated $BTC value. Typically, these physical Bitcoins are inscribed with a code that allows the owner to access actual $BTC on the Bitcoin blockchain.
The appeal of physical Bitcoins is mostly aesthetic. For example, you could write your Bitcoin wallet’s seed phrase on a piece of paper and it would have the same effect (except for being less durable).
An early example of physical Bitcoins was made by a company called Casascius. This product was discontinued about a decade ago, in November of 2023. Casascius coins have become somewhat of a collectible and can sell for a price higher than the value of the $BTC they contain.
The Casascius Bitcoins have a private key embedded in the coin and covered by a hologram that displays a honeycomb pattern if it is tampered with. The outside of each coin also contains the first 8 characters of the Bitcoin address associated with the coin. Over the company’s history, Casascius coins were made in versions with ₿0.1, ₿0.5, ₿1, ₿10, ₿25, ₿100 and ₿1,000.

Casascius decided to shut down their business after the Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN) notified the company that their activity meant the company was a money transmitter business and would require the appropriate license.
At the moment, you can purchase “physical” Bitcoin products made by a company called Ballet. This company sells cards inscribed with information to access a certain quantity of Bitcoin. The cards range from 0.1 $BTC on the high end to 0.005 $BTC on the low end. These cards can be an interesting way to have some Bitcoin in cold storage or a gift for a cryptocurrency enthusiast. However, they are sold at a premium to the value of the $BTC they contain.

FAQs
Is Bitcoin real money?
Although Bitcoin isn’t real physical money, Bitcoin can certainly function as real money, and is even accepted as legal tender in some countries (for example El Salvador).
In most places around the world, however, you can’t walk into any given store or cafe and pay for your purchase with a Bitcoin wallet. Still, the adoption of Bitcoin is growing and it’s becoming more and more common to see merchants and service providers accept Bitcoin payments.
How can you tell a fake Bitcoin?
It’s possible that someone would spin up a malicious fork of the Bitcoin blockchain and try to pass it off as the real thing to unsuspecting users.
If you have a Bitcoin wallet and you’re for some reason suspecting that it might be a fake version of Bitcoin, try making another wallet and then sending a test transaction to it. If you receive the transaction and can see it on a Bitcoin block explorer, you’re dealing with real Bitcoin.
Fake Bitcoin is something you’re extremely unlikely to encounter. In practice, most cryptocurrency scams use other methods to steal funds from unsuspecting users.
Most commonly, scammers will try to convince users to deposit their Bitcoin to an “investment platform” where they will be able to earn huge returns on their investment. Once the Bitcoin is deposited to the platform, the scammers will simply cut off communication with the victim and run away with the stolen funds.
If anyone is promising you guaranteed returns if you send Bitcoin to them, you are almost certainly dealing with a scam.
If you don’t have any Bitcoin but want to buy some, make sure that you use a reputable cryptocurrency exchange to do so. Make sure to check out our list of the best cryptocurrency exchanges to learn more.
What does the code for Bitcoin look like?
Different Bitcoin implementations can be written in different programming languages. Satoshi Nakamoto’s original implementation of Bitcoin was written in C++, and this programming language is also used by Bitcoin Core, which is widely regarded as the reference implementation of Bitcoin.
What does a physical Bitcoin look like?
There are two types of physical Bitcoin. The most common type is simply a tangible representation of the idea of Bitcoin. Such representations are usually in the shape of a coin and made out of a gold-colored metal with the Bitcoin logo engraved in the middle. You’ll often see such representations in articles and social media posts discussing Bitcoin.
However, some companies such as Casascius and Ballet have made “physical Bitcoin” products which are tangible items inscribed with the information necessary to access real $BTC coins on the blockchain.
The bottom line
In media, Bitcoin is often portrayed as a golden coin. However, actual $BTC exists only as a digital currency so it doesn’t have a tangible “look” or shape.
The concept of Bitcoin can be difficult to grasp for someone who’s entirely new to cryptocurrency. Therefore, it’s not uncommon to hear people asking what a Bitcoin looks like even though the question seems nonsensical to someone who has a basic understanding of Bitcoin.
If you want to learn more about Bitcoin, make sure to check out our article exploring its mysterious inventor called Satoshi Nakamoto.
 coincodex.com
coincodex.com
