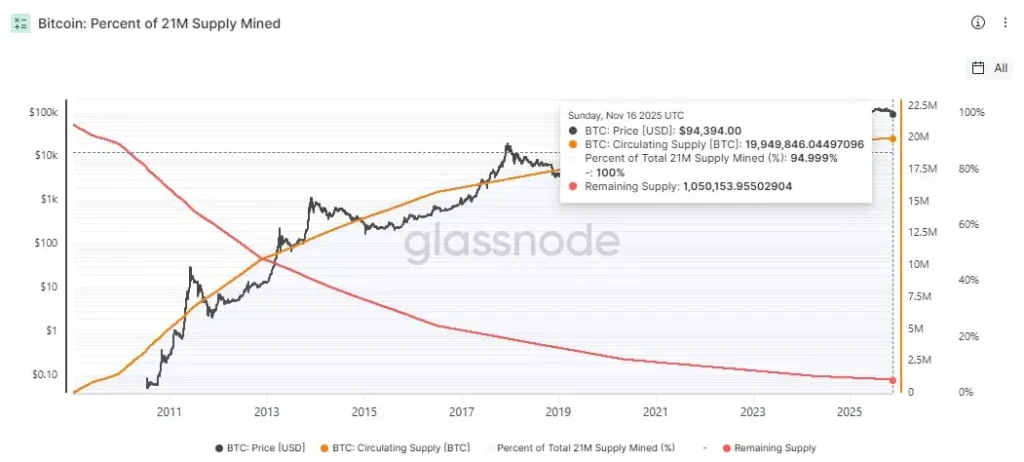
Bitcoin has entered one of the most important chapters of its 17-year history. New data from Glassnode confirms that 95% of the cryptocurrency’s fixed 21 million supply has now been mined. Roughly 19.949 million $BTC is in circulation, leaving just 1.050 million $BTC left to be mined, coins that will enter the market at an increasingly slower pace due to programmed halvings.
Source: Glassnode
The milestone reinforces the cornerstone of Bitcoin’s design: engineered scarcity. With only 5% of supply remaining, Bitcoin’s issuance is transitioning into its slowest and strictest phase yet, making scarcity a central theme for analysts, institutions, miners, and long-term holders tracking the asset’s monetary evolution.
A Supply Milestone Nearly 17 Years in the Making
Satoshi Nakamoto mined Bitcoin’s genesis block on January 3, 2009, embedding a supply schedule intended to prevent inflation, debasement, and discretionary issuance. Today’s 95% threshold marks the latest confirmation that the protocol continues operating exactly as designed.
According to the latest supply breakdown:
- Maximum Supply Cap: 21,000,000 $BTC
- Circulating Supply: 19,949,776 $BTC
- Percentage Mined: 95%
- Issuance Remaining: 1,049,996 $BTC
- Unspendable $BTC Identified: 230.09 $BTC
What remains will be distributed over more than a century due to the halving mechanism, which reduces block rewards roughly every four years. The last Bitcoin is expected to be mined around 2140, long after the current generation of miners has exited the scene.
For economists who analyze digital scarcity, this event is more meaningful than simply crossing a round number. Speaking to Cointelegraph, Thomas Perfumo, a global economist at Kraken, explained that Bitcoin’s annual supply inflation now sits at 0.8%, a rate significantly lower than that of most fiat currencies. According to Perfumo, Bitcoin functions as a “global, real-time and permissionless settlement protocol” whose scarcity resembles the rarity of a masterpiece such as the Mona Lisa.
“This milestone is a reminder of Bitcoin’s resistance against debasement and intervention, operating as designed nearly 17 years later,” Perfumo said.
Yet even with the significance of the milestone, analysts emphasize that its impact does not directly translate to immediate price action. The remaining 5% of supply will take more than 100 years to mine due to the halving schedule, limiting any sudden issuance shock. But structurally, the milestone strengthens the long-term scarcity narrative that Bitcoin has carried since its inception.
Halving Cycles: How Bitcoin Typically Responds as Supply Shrinks
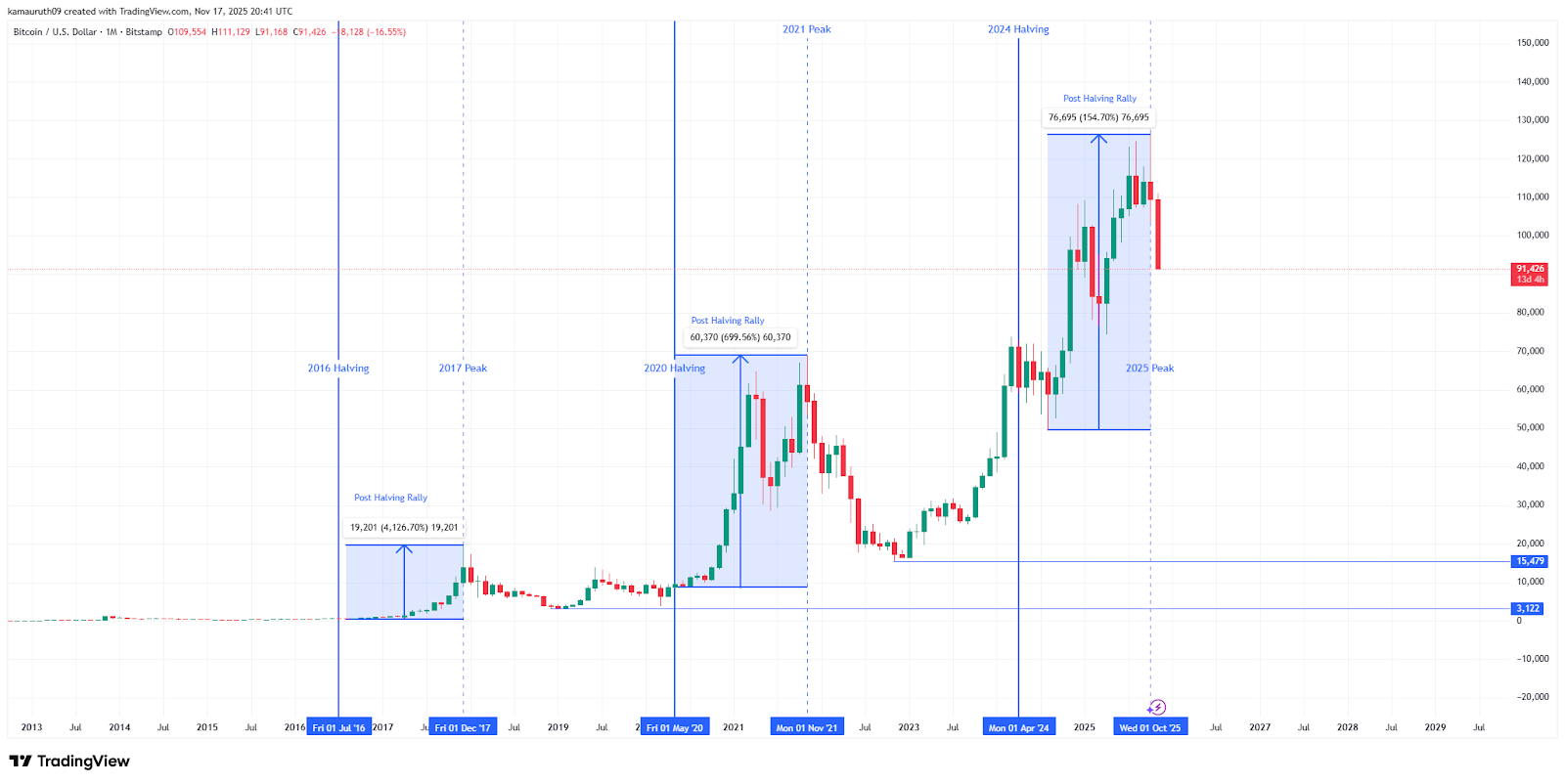
A newly updated long-term monthly chart highlights a recurring pattern: every time Bitcoin’s issuance shrinks through a halving event, a multi-year expansion phase eventually follows. The pattern is not speculative; it is observable data tracked across three completed halving cycles and the current one.
2016 Halving — 2017 Peak
- Halving Date: July 2016
- Post-Halving Rally: an approximate 4,000%
- Peak: Late 2017
- Correction: –84%
This period marked one of Bitcoin’s most dramatic multi-year expansions, driven largely by the first global wave of retail adoption and an emerging understanding of digital scarcity.
2020 Halving — 2021 Peak
- Halving Date: May 2020
- Post-Halving Rally: an approximate 700%
- Peak: Late 2021
- Correction: –77%
Institutional accumulation defined this cycle. MicroStrategy, Tesla, and major asset managers bought large amounts of $BTC, reinforcing Bitcoin’s entry into mainstream finance.
2024 Halving — Current Cycle Status
- Halving Date: April 2024
- Post-Halving High: $126K
- Current Price: $91.4K
- Drawdown: –27%
The pattern mirrors earlier cycles: an initial post-halving surge followed by a mid-cycle correction. Historically, these corrective phases precede long-term expansions. While past performance does not dictate future results, the structural rhythm remains consistent across all cycles examined.
Source: TradingView
As only around one million $BTC remain to be mined, and at a fraction of the pace seen in Bitcoin’s early years, the scarcity dynamic becomes a more powerful force across each subsequent halving.
Mining Economics Shift as Block Rewards Keep Shrinking
The 95% mark has direct implications for miners, whose operations keep the network secure and decentralized. After the April 2024 halving, block rewards fell to 3.125 $BTC per block, placing additional pressure on mining economics.
Jake Kennis, a senior research analyst at Nansen, noted that miners may feel the milestone more sharply than investors. The reduction in rewards forces greater reliance on transaction fees, which represent an increasingly important component of miner revenue.
“Miners are already feeling the impact of reduced block rewards from halvings,” Kennis said. “The 95% milestone underscores this long-term transition, potentially pushing out less efficient miners.”
Network data historically shows that after each halving, weaker mining operations shutter, while stronger, more efficient miners consolidate or reinvest in improved hardware. The long-term trajectory moves the network toward a transaction-fee-dominant model, as envisioned in Bitcoin’s protocol.
Marcin Kazmierczak, co-founder of the oracle provider RedStone, agrees. He sees the milestone as a sign that mining is entering its most transformative era.
“We’re transitioning from block reward-dependent miners to transaction-fee-dependent miners,” Kazmierczak said. “This creates pressure on miners to consolidate or seek efficiency gains.”
Transaction fees already reflect this trend. Periods of network congestion have led to fee spikes, especially during inscription waves. As block subsidies fall, fee markets play a larger role in determining miner priorities and shaping network security budgets.
Scarcity, Institutional Accumulation, and Changing Market Dynamics
While short-term price reactions to the 95% milestone have been subdued, its broader institutional significance is considerable. Bitcoin trades around $91.4K, and although volatility persists, supply scarcity is now viewed as a defining feature in the asset’s macro narrative.
Key structural trends strengthen the scarcity effect:
- Bitcoin ETFs continue accumulating significant amounts of $BTC.
- Institutional demand rises as long-term issuance trends become more visible.
- Exchange reserves sit near multi-year lows, reducing available supply.
- Long-term holders grow their share of all circulating supply.
Kennis notes that the milestone is not a catalyst on its own but reinforces Bitcoin’s “digital gold” identity. Analysts highlight that scarcity is only part of Bitcoin’s value; it is the combination of fixed supply, predictable issuance, decentralization, and global liquidity that drives long-term interest.
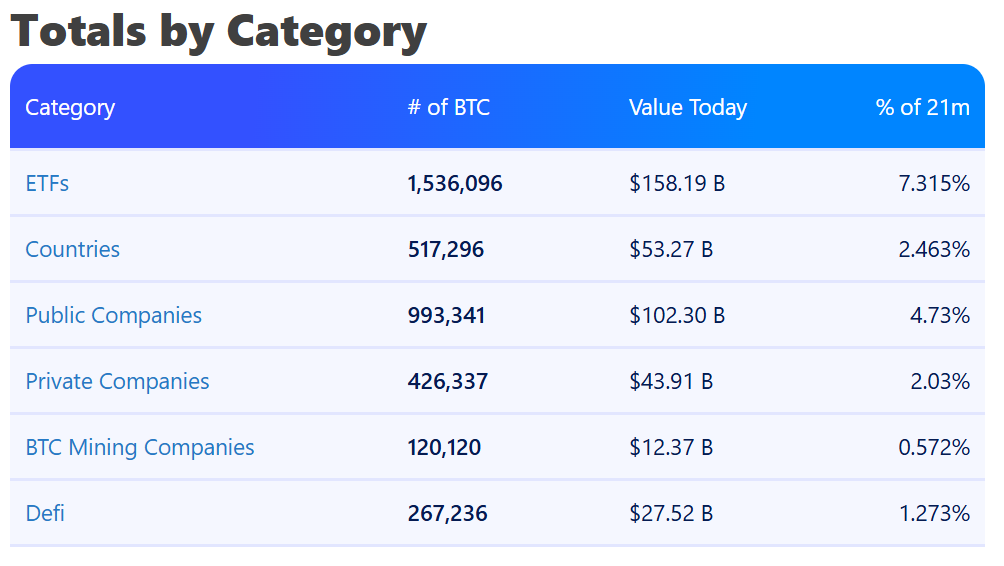
External data further shows that around 17% of all Bitcoin is held by public companies and countries, reducing the free-floating supply even further and amplifying supply-demand imbalances when the market heats up.
Source: BitBo
Kazmierczak believes the milestone signals Bitcoin’s maturation, shifting the asset from a growth-phase instrument into a fixed-supply monetary asset with clearer long-term characteristics.
“The real inflection points were earlier in the supply curve,” he said. “This milestone represents Bitcoin’s maturity—we’re moving toward predictable long-term scarcity.”
What the 95% Milestone Signals for the Next Era of Bitcoin
Crossing the 95% mark is not an isolated event. It represents a convergence of factors that have been building for years:
- Shrinking annual issuance
- Halving-driven reward reductions
- Rising mining difficulty
- Fee-based security models
- Institutional accumulation
- Lower exchange liquidity
- A growing number of long-term holders
Each halving makes Bitcoin’s scarcity more pronounced, each cycle distributes fewer new coins, and each new milestone shifts the asset’s economic center of gravity toward long-term holding.
The historical data across cyclical charts captures the same multi-year rhythm: tightening supply — post-halving expansion — mid-cycle correction — new structural growth.
With only 5% of supply remaining, Bitcoin now enters the most scarcity-intensive phase of its issuance timeline. The milestone signals a clear transition point, one that deepens scarcity, reshapes mining incentives, and anchors long-term accumulation strategies across the global market.
 cryptonews.net
cryptonews.net
