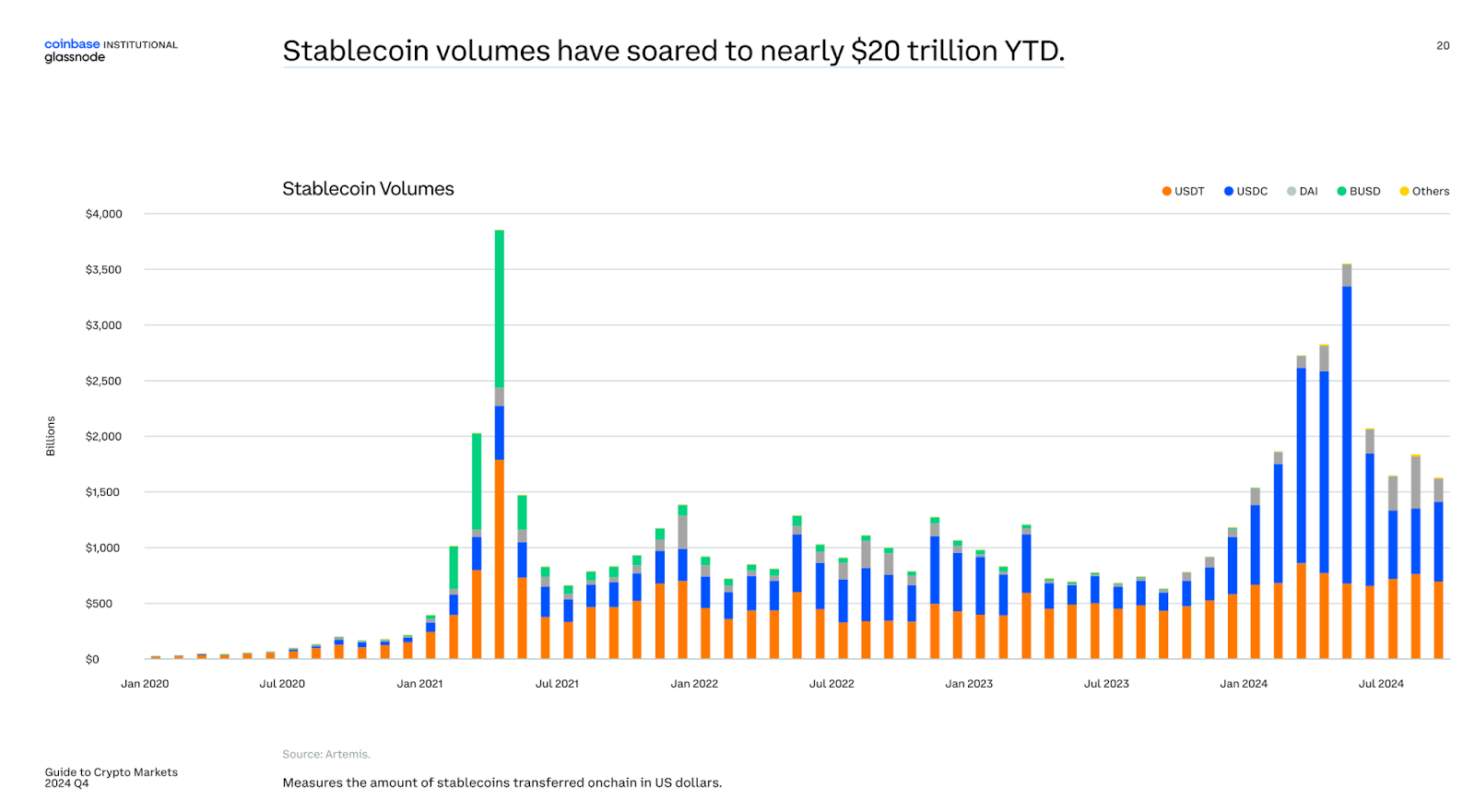
The third quarter of 2024 saw a surge in stablecoin use and adoption, according to Coinbase’s 4th Quarter Guide to Crypto Markets report with Glassnode.
Stablecoins hit an all-time high market capitalization of nearly $170 billion in Q3 2024, according to the report. This growth occurred alongside the implementation of the European Union’s new Markets in Crypto-Assets regulation, which introduced clearer rules for stablecoin operations.
Stablecoins have become a key tool for users seeking faster, cheaper, and more secure transactions. Their utility in payment systems, including remittances and cross-border transfers, has continued to expand.
Recently, Anthony Pompliano argued that tech innovations outside of crypto could lead to a new era in which stablecoins become the primary transaction medium in a machine-driven economy. This increased adoption reflects the growing role of stablecoins in crypto trading and real-world financial systems.
According to the report, stablecoin volumes have reached nearly $20 trillion year-to-date as of the third quarter, indicating their growing role in the global economy.
Stablecoin and Bitcoin dominance
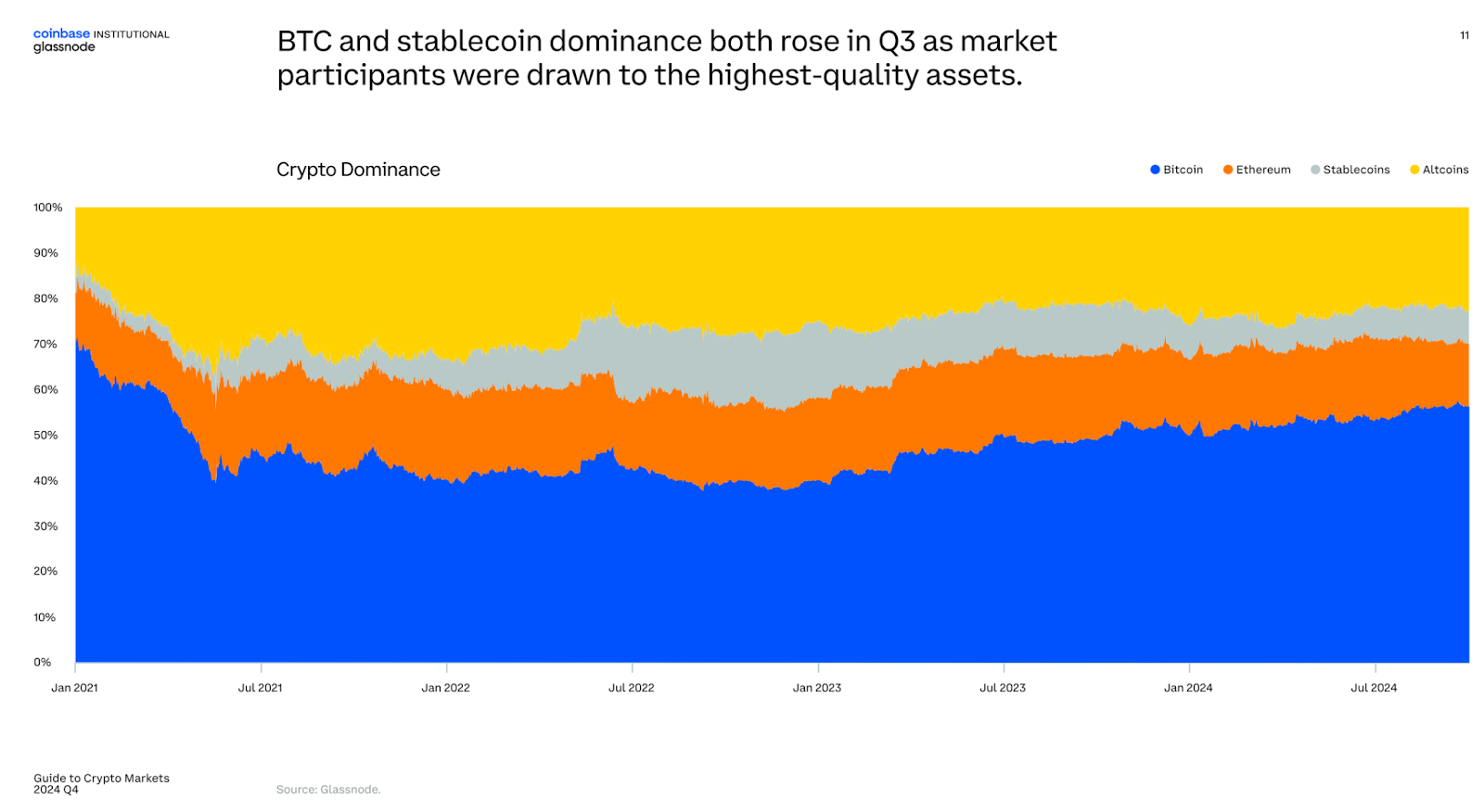
Stablecoin dominance also increased in Q3 alongside Bitcoin (BTC), with crypto investors gravitating toward what they see as the highest-quality digital assets.
The current BTC cycle closely tracks the 2015-2018 and 2018-2022 cycles, which ended with nearly 2,000% and 600% returns, according to the report.
What is MiCA?
The Markets in Crypto-Assets Regulation is a comprehensive framework enacted by the European Union in June 2023 to regulate the crypto industry across its 27 member countries. It initiates a 12-18 month transition period for implementing rules on anti-money laundering, combating the financing of terrorism and digital asset custody, among others.
MiCA’s impact on stablecoins still remains to be seen, but Tether (USDT) CEO Paolo Ardoino expressed concern that MiCA’s 60% cash reserve requirement for stablecoins could create systemic risks for European banks. He argued that such regulations might exacerbate liquidity issues during large-scale redemptions, potentially leading to bank failures.