While the U.S. recently marked the longest period of inverted bond yields in history, surpassing two years, data indicates that a total of 26 countries now have an inverted yield curve. Investors and economists closely monitor yield curve inversions, as they have historically signaled an increased likelihood of economic recessions.
From the U.S. to Europe: 26 Countries Grapple with Inverted Yield Curves
Current statistics reveal that the inverted yield curve phenomenon is not confined to the United States. Other nations are also experiencing yield curve inversion or flattening. An inverted yield curve occurs when long-term bond interest rates fall below short-term rates.
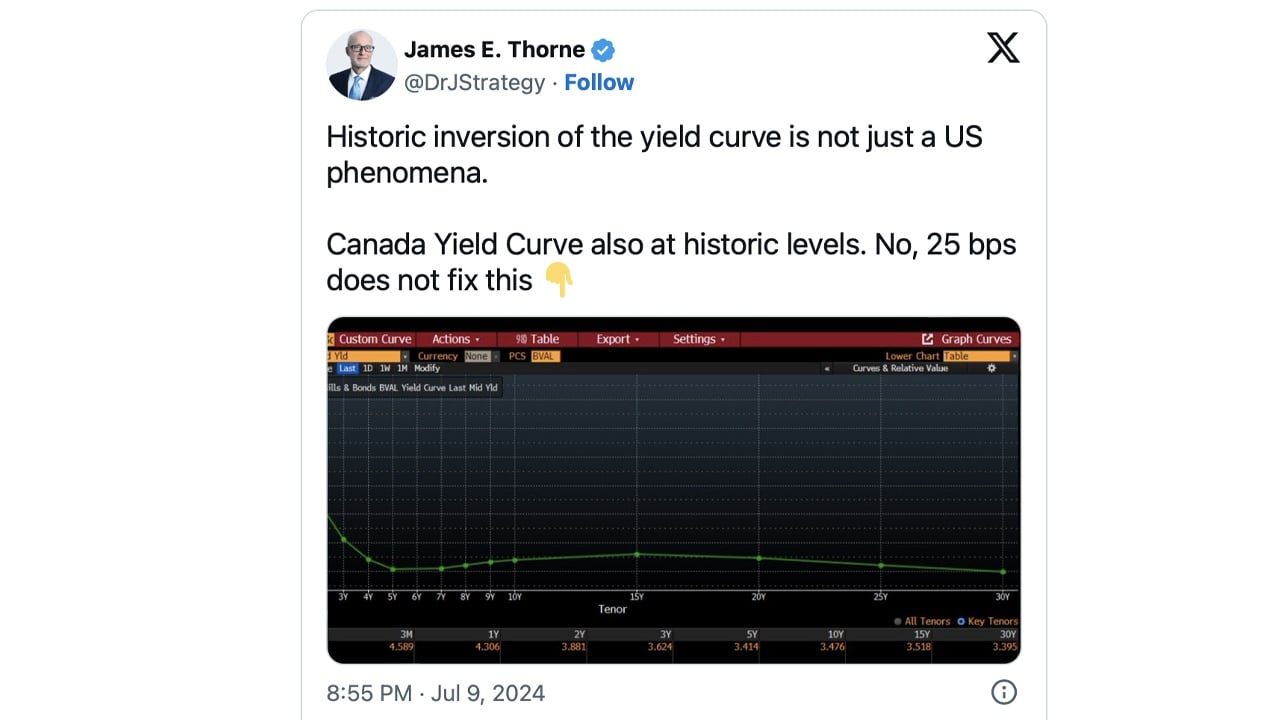
Typically, longer-term bonds offer higher yields to compensate for the risk over a more extended period. However, in an inverted yield curve situation, investors demand higher yields for short-term bonds, reflecting concerns about the economy’s immediate outlook.
Bitcoin.com News has frequently reported on the inverted yield curve in the U.S., which recently reached its two-year milestone, the longest in the country’s history. However, the United States is not alone in facing this bond market anomaly; data shows that 26 countries, including 17 with A to AAA ratings from S&P, have inverted yield curves.
Historically, an inverted yield curve has preceded economic downturns, leading investors to anticipate a recession. Countries currently experiencing an inverted yield curve include Iceland, Malta, Canada, Denmark, Norway, Qatar, Germany, Sweden, Singapore, Ireland, Hong Kong, and Austria. Additionally, nations without triple-A ratings, such as Russia and Pakistan, also show an inverted yield curve.
Given the widespread incidence of inverted yield curves, the signals are not favorable. As multiple countries, including those with top credit ratings, face this economic anomaly, the potential for a global economic downturn looms large. The prolonged nature of these inversions historically foreshadows recessions, raising concerns about the near-term economic outlook worldwide.
What do you think about the 26 countries facing inverted yield curves? Do you think it is concerning? Share your thoughts and opinions about this subject in the comments section below.
 news.bitcoin.com
news.bitcoin.com