SlowMist, a prominent blockchain security company, has given a warning on an advanced phishing attack on users of MetaMask. SlowMist Chief Security Officer, who goes by the alias 23pds, warned the crypto community of an increasing threat of fake MetaMask domains, which are used to steal sensitive information on January 5, 2026. The attack consists of several fraudulent steps that use the trust that the user has in security measures, including 2FA checks, to steal valuable wallet contents, among which are recovery phrases.
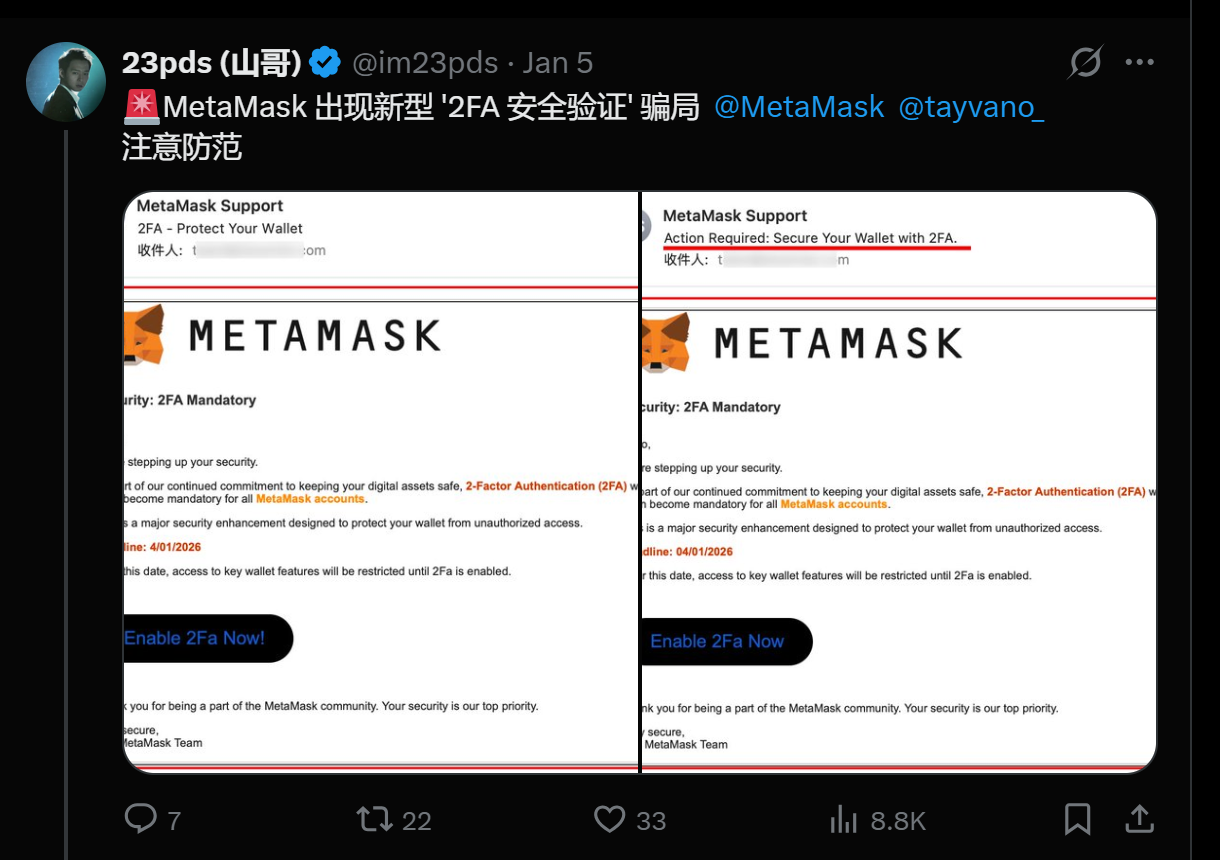
The fraud starts with a set of attackers registering fake domains whose names are similar to the legitimate one of MetaMask. As an example, a user can be deceived to enter the site named mertamask and not the original metamask. Once joining the scam world, the victims are sent to a website that appears to be a real MetaMask security warning.
The hackers then display a bogus 2FA authentication page, full of countdown clocks and safeties. The goal of this fake interface is to gain trust where the user is requested to insert their seed phrase by pretending that it is an authentication procedure. Before the victim passes his or her recovery phrase, the attackers will have complete access to his or her wallet.
Source: X
Decreasing Phishing Losses But Evolving Attacks
A new report states that phishing losses decreased by 83%, with the amount that was close to $494 million in 2024 reducing down to $83.85 million in 2025. The affected users also reduced by 68 % and this was an annual change of around 330,000 users to 106,000.
Although the overall loss has decreased, the MetaMask 2FA scam is a good wake-up call that threat actors are still improving their skills. According to the analysts in the field of security, phishing is still firmly associated with the overall market practices, including trading volumes and crypto rallies. Indicatively, Ethereum recorded the greatest losses in 2025 when the project was very strong in the third quarter and its losses on phishing were almost $31 million.
The reduction in the number of losses was not related to the reduction in attacks but to change of strategy. The attackers have changed the trend to mass retail campaigns instead of high-profile, large-scale stealing. Although the number of cases over 1 million in 2025 is only 11, versus 30 the previous year, attackers have resorted to emptying smaller sums of money of a greater number of victims. The retail user was experiencing less focus on isolated, high-value targets as the average loss per victim in 2025 was 790.
The most useful attack vectors in 2025 were Permit and Permit2 approvals, which caused 38% of the losses in the cases that surpassed $1 million. The Ethereum Pectra upgrade also introduced new ways of attacks, and attackers took advantage of EIP-7702-based malicious signatures. These signatures allow several malicious activities to be packed into one user consent posing more threats to wallet holders. There were two incidents of this exploit in August 2025 resulting in a total loss of $2.54 million.
Major wallet providers, such as MetaMask, Phantom, WalletConnect, and Backpack, have come together in an effort to create a global network of phishing defense in reacting to the ongoing threats. This is because, in a partnership with the Security Alliance (SEAL), an immune system has been developed that is decentralized and aimed at detecting and combating phishing in real time.
The SEAL system enables users and researchers to report phishing activities across the globe and the process is automatically verified and distributed among the involved wallets. The project will enhance quicker response rates and minimize the cost of phishing attacks. Besides, SEAL has a verifiable phishing report tool that allows security professionals to show the authenticity of the phishing sites to enhance overall threat detection.
One of the Threats on the Rise: Deepfakes and Other Attack Vectors.
In April 2025, Manta Network co-founder Kenny Li announced that he was the victim of a high-tech attack involving deepfake. In one of the Zoom calls, the attackers had recorded videos of known people and integrated them into the conference and duped Li to install malicious software under the guise of Zoom updates. It is estimated that this attack is associated with the Lazarus Group, which is a hacking group that has an alleged connection to the North Korean country.
Hack-related and other cybersecurity exploits linked to crypto-related losses also plummeted greatly in December 2025, and it decreased by 60 percent to about $76 million, a decrease compared to November when it stood at 194.2 million. Nevertheless, specialists warn that some old-time attacks, including address-poisoning scams and browser wallet attacks, remain active against users, and these examples demonstrate the persistent difficulty in the security of crypto assets.
The industry has been able to take the step in the defense sector, the key players in the wallet industry have come together to fight phishing. The dynamic nature of the attackers implies that security practices should keep changing. Users have to be more careful and guarded when carrying out security measures, especially when asked to insert such sensitive wallet information as recovery phrases. The development of phishing traps goes on, which is why collaboration between users and service providers is necessary to guarantee the safety of the larger crypto ecosystem.
 cryptonews.net
cryptonews.net
