The digital landscape continues to evolve, with the Internet Computer ($ICP) protocol potentially playing a significant role in this change. $ICP aims to decentralize the internet using blockchain technology, offering increased capacity and presenting potential opportunities for developers, entrepreneurs, and users. However, it is important to consider both the advantages and challenges associated with this innovative approach.
In this article, BeInCrypto explores $ICP’s impact on democratizing web infrastructure and the advancements in smart contract capabilities.
We also examine the project’s rise and fall, exploring the reasons behind its spectacular downfall and the lessons to be learned from its trajectory.
Democratizing Web Infrastructure: Breaking Monopolies and Fostering Inclusivity
For years, the internet has been dominated by tech giants and government institutions, controlling large swathes of the digital space. $ICP seeks to disrupt this status quo by decentralizing web infrastructure and empowering individuals to access and develop on the internet freely.
Pros: A More Inclusive Internet
One of $ICP’s primary advantages is fostering a more inclusive, accessible internet. By breaking down barriers to entry and reducing reliance on centralized platforms, the protocol empowers smaller businesses and entrepreneurs to compete with large corporations.
This shift enables a fairer, more competitive market and sparks innovation in the digital space.
Cons: Scalability and Security Concerns
However, $ICP’s decentralization comes with potential drawbacks. Decentralized systems can face scalability issues, and ensuring adequate security becomes increasingly challenging.
While $ICP’s architecture aims to mitigate these concerns, they still pose potential risks to users.
Smart Contract Advancements: Revolutionizing Industries
$ICP’s enhanced smart contract capabilities are transforming industries like finance, healthcare, and supply chain, driving innovation and efficiency.
Pros: Unprecedented Flexibility and Speed
$ICP’s smart contracts offer flexibility and speed, enabling secure, tamper-proof automation of complex processes.
With $ICP, industries can streamline operations, reduce costs, and improve overall efficiency, all while maintaining a high level of security and trust.
Cons: Adoption and Integration Barriers
Nonetheless, smart contracts on $ICP are not without obstacles. Integrating these revolutionary contracts into legacy systems may prove challenging, and gaining widespread adoption might be slow due to hesitance from traditional industries. While $ICP has the potential to transform sectors, its success depends on overcoming these barriers.
Developer Frontier: The Opportunities and Challenges of Decentralized Applications
$ICP’s technology allows developers to build open, decentralized applications, leading to a new era of innovation and collaboration.
Pros: A Platform for Innovation
Developers can harness $ICP’s decentralized infrastructure to build novel applications and services, free from the constraints of centralized platforms. This environment fosters collaboration, cross-pollination of ideas, and rapid innovation, ultimately benefiting end-users and the broader digital ecosystem.
Cons: Complexity and Learning Curve
However, the complexity of $ICP’s technology may present challenges for developers. Building decentralized applications requires learning new programming paradigms, and the intricacies of $ICP’s system can be daunting. Consequently, some developers may struggle to adapt or be reluctant to adopt the protocol.

The Rise and Fall of Internet Computer: Lessons from a Blockchain Giant
Internet Computer took the world by storm in 2021, with a meteoric rise in its token value and a promise to disrupt the cloud computing industry. However, less than two years later, the project has experienced a spectacular fall from grace. In this section, we explore the reasons behind $ICP’s downfall and the lessons that can be learned from its trajectory.
A Promising Start: The Launch of Internet Computer
The Internet Computer project was launched by DFINITY, a Swiss non-profit organization, amidst a frenzy of excitement for new cryptocurrencies. As a result, its token, $ICP, soared in value, and the project quickly became one of the world’s top ten largest coins. With over $166 million in funding from reputable investors such as Andreessen Horowitz and Polychain Capital, Internet Computer seemed poised to revolutionize the digital landscape.
The project aimed to build a decentralized supercomputer capable of running blockchain-based applications comparable to popular services like WhatsApp and Venmo. This ambitious vision garnered significant attention, with some even claiming that Internet Computer could disrupt giants like AWS and Google Cloud.
The Downfall: Unfulfilled Promises and Lack of Adoption
Despite its initial hype and substantial funding, Internet Computer has failed to live up to expectations. The $ICP token’s value plummeted by over 98%, and its total market cap plunged from $9.5 billion to around $1 billion.
Opacity and Lack of Development
One of the primary factors contributing to Internet Computer’s downfall is the lack of transparency regarding its ecosystem. Unlike other popular blockchains like Ethereum, Polkadot, and Binance Chain, it is difficult to ascertain what has been built on Internet Computer. Many of the apps in its ecosystem have either ceased development or show little to no activity.
Unsuccessful dApps and User Experience Issues
Internet Computer’s dApps, like OpenChat and DSCVR, have faced challenges in gaining user adoption. The process of creating an account on OpenChat, for example, is lengthy, and new members are no longer being accepted. Similarly, DSCVR, a community-owned professional network, lacks meaningful content, leading to a disappointing user experience.
Other dApps, such as DFinance, Portal, and NFT Studio, have faced similar issues, with little to no meaningful activity in their ecosystems.
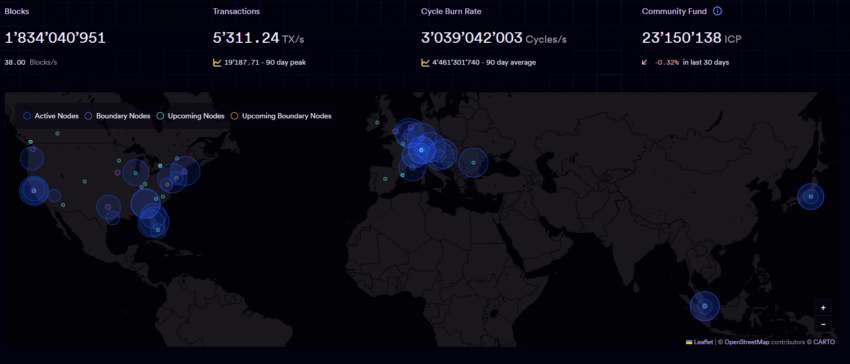
A Glimmer of Hope: Internet Computer’s Remaining Activity
Despite its struggles, Internet Computer is not entirely dead. Activity within its ecosystem still exists, as evidenced by its explorer. The question remains, however, whether this activity justifies a market cap of over $1 billion.
Lessons Learned and the Future of Decentralized Technology
Internet Computer’s meteoric rise and subsequent fall offer valuable insights into the volatile nature of the cryptocurrency and blockchain industry. While its ambitious goals and substantial funding initially garnered excitement, the project’s inability to deliver on its promises and the lack of user adoption ultimately led to its downfall.
As the world of decentralized technology continues to evolve, projects like Internet Computer serve as cautionary tales. To succeed in this competitive landscape, blockchain projects must offer transparent development, user-friendly experiences, and the ability to adapt to changing market conditions. Only then can they hope to achieve lasting impact and growth in the digital ecosystem.
 beincrypto.com
beincrypto.com
