A recent United Nations report revealed that 50% of North Korea’s foreign income is attributed to cyberattacks and thefts. The UN detailed that between 2017 and 2023, numerous crypto-related businesses fell victim to these cyber operations. These cyber operations are not only a means of income but are directly linked to funding approximately 40% of North Korea’s weapons of mass destruction programs. The estimated financial toll of these hacks stands at a staggering $3 billion.
The findings of the UN report are consistent with previous estimates from the United States, with additional support from the 2023 report by blockchain analysis firm Chainalysis, highlighting a year full of crypto platform vulnerabilities tied to North Korea.
Joe Dobson, a senior cybersecurity expert, emphasizes that DPRK hackers are keen observers of technological evolution. This adaptability was demonstrated by their use of Tornado Cash, a tool for obfuscating the origins of stolen Ethereum, to launder approximately $12 million worth of ETH.
The Lazarus Group was identified as a primary user of Tornado Cash, highlighting a shift in their laundering operations following the closure of services like Sinbad.io and Blender.io.
The North Korean hackers funneled over $100 million worth of Ethereum through the prohibited cryptocurrency mixer, Tornado Cash, in just the past week. Blockchain security firm PeckShield reports that associated addresses, linked to the exploitation of the HTX exchange and Heco Bridge, both related to Justin Sun, channeled 40,391 ETH (approximately $145.7 million) through Tornado Cash, a decentralized crypto mixing tool.
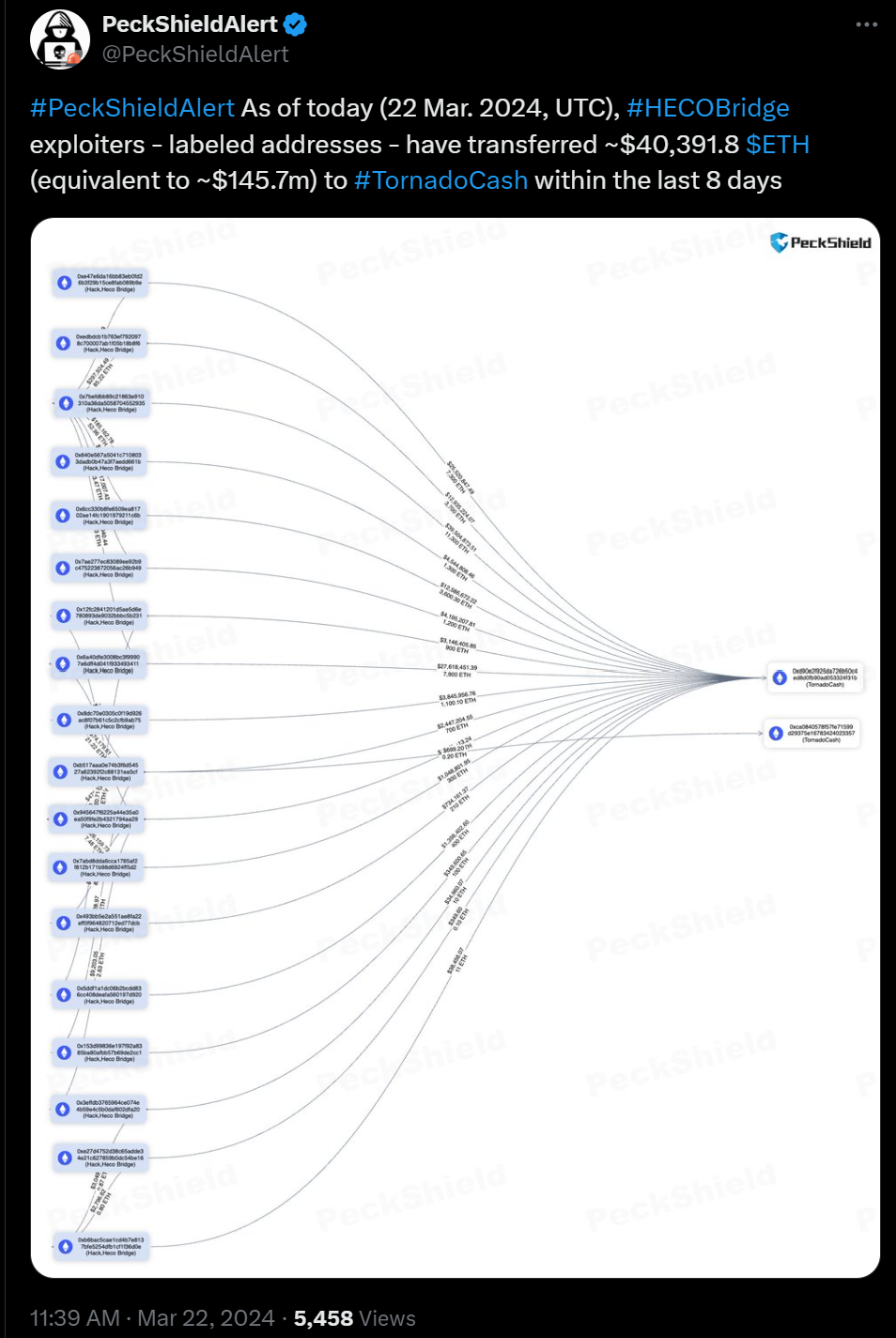
The funds were dispersed through 18 different addresses to two specific Tornado Cash addresses, marking the first movement of these assets since their theft in November during the HTX and Heco bridge hack, widely attributed to the North Korean hackers. Blockchain analytics firm Elliptic highlights the challenges authorities face in curbing the operations of decentralized mixers like Tornado Cash, which remain operational despite being banned.
A Year of Heists
Over $750 million was pilfered from various crypto projects last year alone, with North Korean hackers linked to major thefts, including the $41 million hack of the online casino Stake and the $100 million theft from Atomic Wallet. This recent maneuver by the Lazarus group is part of a larger pattern of cyber thefts that have collectively netted approximately $3 billion from 2017 to 2023.
According to blockchain analytics firm Chainalysis, there were 20 documented cyberattacks by North Korea in 2023, an increase from 15 in the previous year. Despite the increase in attacks, the estimated value of stolen assets by North Korea-linked hackers saw a decline, dropping to $1 billion in 2023 from $1.7 billion in 2022. This decrease is attributed to the bear market, which adversely affected the value of virtual assets.
The issue of cryptocurrency hacks is not isolated to North Korea. Globally, there were 231 cryptocurrency hacks in 2023, a slight increase from 219 in 2022. However, the total estimated value of stolen assets fell by 54% to $1.7 billion. Attackers are continuously refining their techniques, exploiting vulnerabilities in smart contracts, and utilizing new laundering methods through platforms known as mixers.
North Korea’s increased weapons tests, aggressive rhetoric, and cooperation with countries like Russia have intensified global apprehensions regarding its military ambitions. The U.S., along with allies in South Korea, Japan, and Southeast Asia, remains committed to countering North Korea’s illicit cyber activities.
Who Has Been Hit in 2024?
According to CNN, various platforms across decentralized finance (DeFi), exchanges, and other crypto-related services have been hit with hacks cumulating in losses totaling over $455.1 million. These incidents highlight the persistent vulnerabilities and the urgent need for enhanced security measures within the industry.
Mozaic Finance, a DeFi platform, reported a $2.4 million loss due to a security breach on the Arbitrum chain on March 15, 2024. A compromised private key led to unauthorized transactions, prompting swift action from Mozaic to mitigate the damage. BitForex, a cryptocurrency exchange, disappeared with nearly $57 million from its hot wallets on February 23, blocking users’ access. Its absence among the platforms flagged by Hong Kong’s Securities & Futures Commission points to regulatory challenges in identifying risky entities.
PlayDapp, a crypto gaming and NFT platform, suffered from the unauthorized minting of 1.79 billion PLA tokens, valued at over $290 million, in February. Despite attempts to negotiate with the attacker, the funds were not recovered, demonstrating the difficulties in managing such crises.
Abracadabra Finance lost approximately $6.5 million due to a hack on January 30, affecting its stablecoin, Magic Internet Money (MIM). The incident, caused by a smart contract vulnerability, briefly destabilized MIM’s market value.
Concentric.fi faced a $1.8 million loss from a social engineering attack. The incident’s connection to a previous exploit on the OKX decentralized exchange suggests the involvement of the same perpetrator(s). Socket.Tech was exploited for $3.3 million on January 16, impacting Bungee Exchange. The attack underscored the risks of granting unlimited access to funds through protocols.
Gamma Strategies reported a $3.4 million loss due to an exploited vulnerability in its DeFi protocol, illustrating the complex risks associated with digital asset management. CoinsPaid, a digital asset processor, also experienced a $7.5 million hack involving unauthorized withdrawals. This was its second major security breach within six months, underlining the ongoing threat of sophisticated cyber-attacks.
Radiant Capital halted its operations on the Arbitrum network following a $4.5 million flash loan attack. This incident raises concerns over the security of newly introduced markets and the importance of rigorous codebase reviews. Orbit Chain lost over $80 million due to compromised multisig signers, highlighting significant security flaws in private key management and the need for enhanced protections.
These incidents collectively underscore the critical importance of robust security frameworks, transparent incident response strategies, and regulatory oversight to safeguard stakeholders within the rapidly evolving cryptocurrency landscape.
 cryptonews.net
cryptonews.net