2018 was a booming year for the hackers executing their malicious mining events although the bears ruled the cryptocurrency market the entire year. These individuals found loopholes in the cryptocurrency mining industry to monetize their skills. Much vulnerability got exploited with the industrialization and advancement of malicious cryptocurrency miners.
Also, applications with improper permission configurations and weak passwords on cloud servers have become major targets for many malicious mining activities. As it stands, hackers will continue to exploit all vulnerabilities associated with cryptocurrency mining and may use them as foundations to launch further attacks.
Attack Tendency
The now infamous 0-day and N-day vulnerabilities have become the entries for the malicious crypto miners. Users are required to fix 0-day vulnerabilities in a restricted amount of time.
Last year, several widely used web applications were affected by high-risk vulnerabilities resulting in major security threats to the whole Internet.
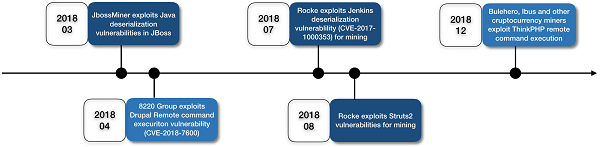
The security community analyzed all the vulnerabilities data and shared all the details found making exploit scripts accessible on the Internet. Hackers never give up these ‘entries’ with some N-day vulnerabilities often exploited by malicious cryptocurrency miners. The Alibaba Cloud has noted that the duration between disclosure and large-scale exploitation of 0-day vulnerabilities is gradually getting shorter.
For instance, the JBoss deserialization vulnerabilities were discovered in May 2017. The large-scale exploitation done by JbossMiner started from the end of 2017 and got to its highest levels in March 2018. Last year, the time interval from exposure of Drupal and ThinkPHP remote command execution vulnerabilities to their significant exploitation was less than one month.
Non-web-based applications
These types of applications exposed to any public networks are a favourite target for the malicious miners. The enterprises security teams focus on WAF, RASP, and vulnerability scanning products while somehow neglecting the non-web applications that are not core applications of enterprises. The most affected applications include ApsaraDB for Redis, Hadoop, and SQL Server.
Therefore, high-risk vulnerabilities often remain unfixed enabling cryptocurrency mining hijackers to exploit these persistent vulnerabilities on the internet. For instance, the DDG botnet continues exploiting the illegal access to ApsaraDB for Redis.
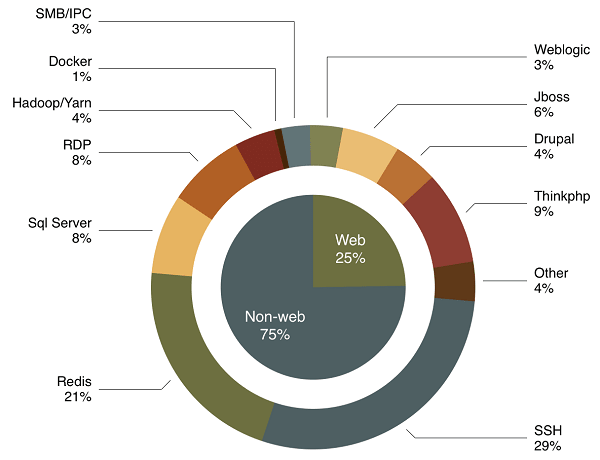
Brute-force Attacks
The hackers widely exploit the brute-force attacks to distribute attacks and it works for the hackers since weak passwords are still widespread on the internet. In most cases, the SSH, RDP, and SQL Server applications are the major interests for the malicious cryptocurrency miners. The applications get compromised by mining viruses distributed by brute-force attacks against weak passwords.
Mining Trojans
Once the mining Trojans get planted in the compromised hosts, the cryptocurrency mining hijackers continue to control these hosts. Moreover, they use them to scan and also attack other hosts using malicious tools such as DockerKiller, DDG, and RDPMiner. The Trojans are known to spread quickly and are considerably difficult to eliminate since they target hosts compromised by malware to attack other hosts.
Whenever the attacked hosts have configuration or vulnerability issues, they quickly succumb to the attack. Several hijackers also directly control some hosts to initiate network attacks. 8220 is a renowned malicious cryptocurrency miner of this type that attacks successfully but never spreads further. The malicious miner uses multiple vulnerability exploitation techniques featuring fast vulnerability update speed.
The mining trojans normally spread like worms and capitalize on their value by persisting on the compromised hosts. In the Linux systems, cryptocurrency mining hijackers employ crontab to set commands that are executed regularly. They also use
Cryptocurrency mining hijackers are also known to avoid security analysis. They also trail trace through disguised processes, code obfuscation, shell-protection, and private mining pools (via proxy).
Drupal Issue
As security measures are getting improved and enhanced, the mining hackers are also stepping up their activities. There is another remote code execution that was recently revealed in Drupal. One exploit that is still working currently has been used many times in unsuccessful attacks against Imperva customers. The number of attacks on other websites is unknown and some may likely be successful.
Hence, users who do not fix high-risk 0-day vulnerabilities in time are most likely to suffer from malicious mining. Upgrade to Drupal 8.6.10 version in the case that you are using the Drupal 8.6.x version. On the other hand, if you are using Drupal 8.5.x or earlier versions, upgrade to Drupal 8.5.11.
Always install any available security updates for contributed projects after updating Drupal core. Please note that there is no core update necessary for Drupal 7, but several Drupal 7 contributed modules do need updates. Versions of Drupal 8 that came before the 8.5.x are end-of-life and do not get any security coverage.
Drupal is a content management system that resembles wordpress.
 cryptovibes.com
cryptovibes.com