There are plenty of layer 1 blockchains out there. That means that there is stiff competition in this field, which makes it also a healthy environment. Remember, only the strong survive. But who will be that survivor?
There are a couple of ways to see which criteria will make a difference. Lucas, a senior intern at Bankless, wrote a Twitter thread about 5 indicators to evaluate blockchains. We think they are going to be helpful. So, let’s dive in and see what we need to look out for.
Bitcoin, Ethereum, Solana, Avalanche, Cosmos, Polkadot…
The Layer 1 landscape is competitive.
How do you evaluate which one could come out on top?
Here are the 5 questions you need to answer:
🧶
— Lucas 🔥_🔥 (@0x_Lucas) July 6, 2022
1. Security
Layer 1 blockchains are settlement layers for value. Their function is to provide a secure and immutable ecosystem. In this case, what makes a blockchain secure is its consensus mechanism, which has advanced cryptographic models. On the other hand, the immutable feature of a blockchain refers to its ability to avoid modifications to confirmed blocks.
Moreover, you can measure blockchain security in these two ways.
a) How Much Does It Cost to Attack the Network?
The only way to effectively attack a blockchain is to do it to 51% of its hash rate. So it makes sense if only a few people control network nodes, it is easier for them to agree and attack it. This is most likely to happen in smaller networks.
Understand more about 51 % Attack.#BTC #ETH #wazirXwarriors #Blockchain #Attack pic.twitter.com/QOmotZdAQt
— Nikhil D Prince 🇮🇳 (@NikhilDPrince) September 21, 2020
Another well-known attack form is the Sybil attack. Here, the attacker will flood a network with many pseudonymous nodes. These can influence a network.
b) How Much Do Validators Receive as Rewards, to Be Honest Actors?
A validator is the same as a network node. They assist in processing and validating new blocks. This allows them to add the blocks to the chain. On a PoW blockchain, this means mining, on a PoS blockchain we refer to this as staking.
The reward amount that validators earn varies between blockchains. Being a validator sometimes asks for a hefty investment. So, the reward must outweigh the investment. For example, bitcoin currently has 12 mining pools worldwide. See the picture below:
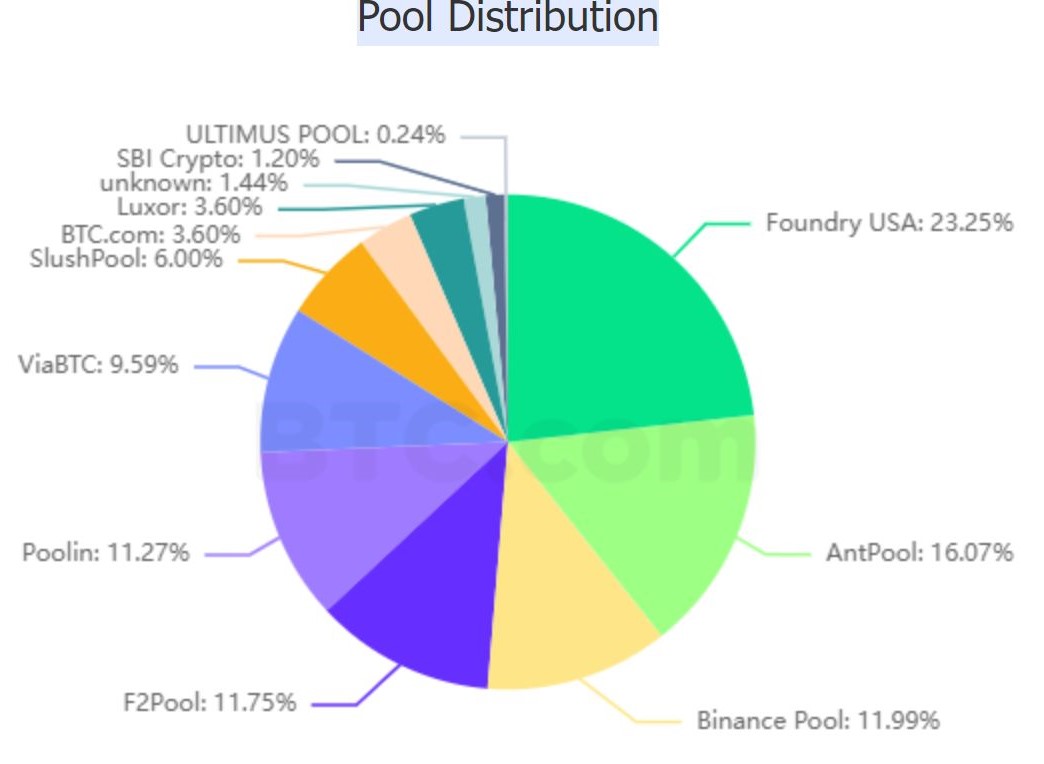
Source: BTC.com
2. Decentralization
In case anyone cannot take part in validation or run a node, the blockchain will not be decentralized. In that case, you can use AWS (Amazon Web Services). This is a fully managed service. It allows you to quickly create and deploy blockchain networks. However, blockchains with this feature cannot be called “decentralized”.
In the following picture, you will see how many validators each layer 1 blockchain has. The more nodes there are, the more decentralized.
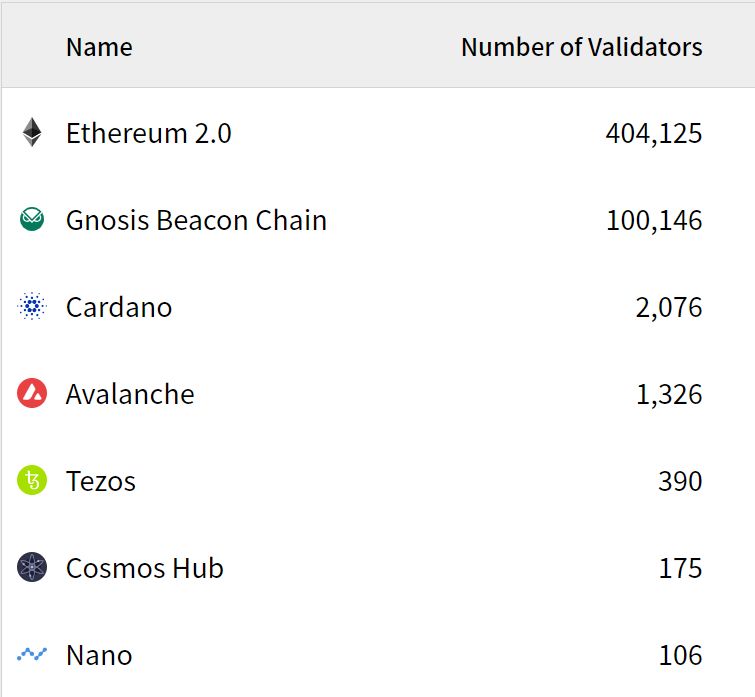
Source: Stakers.info
3. Number of Developers
This is a crucial question. If there are no developers, there are no apps. Without apps, there are no users. If a project has no users, there’s no value.
So, devs are worth their weight in gold, as Peter Schiff would say. This is where the bucket stops when a blockchain doesn’t have developers who build use cases. Ethereum has the most, with well over 200 active developers per month in 2021.
The picture below gives you an idea of how many developers work on a variety of blockchains.
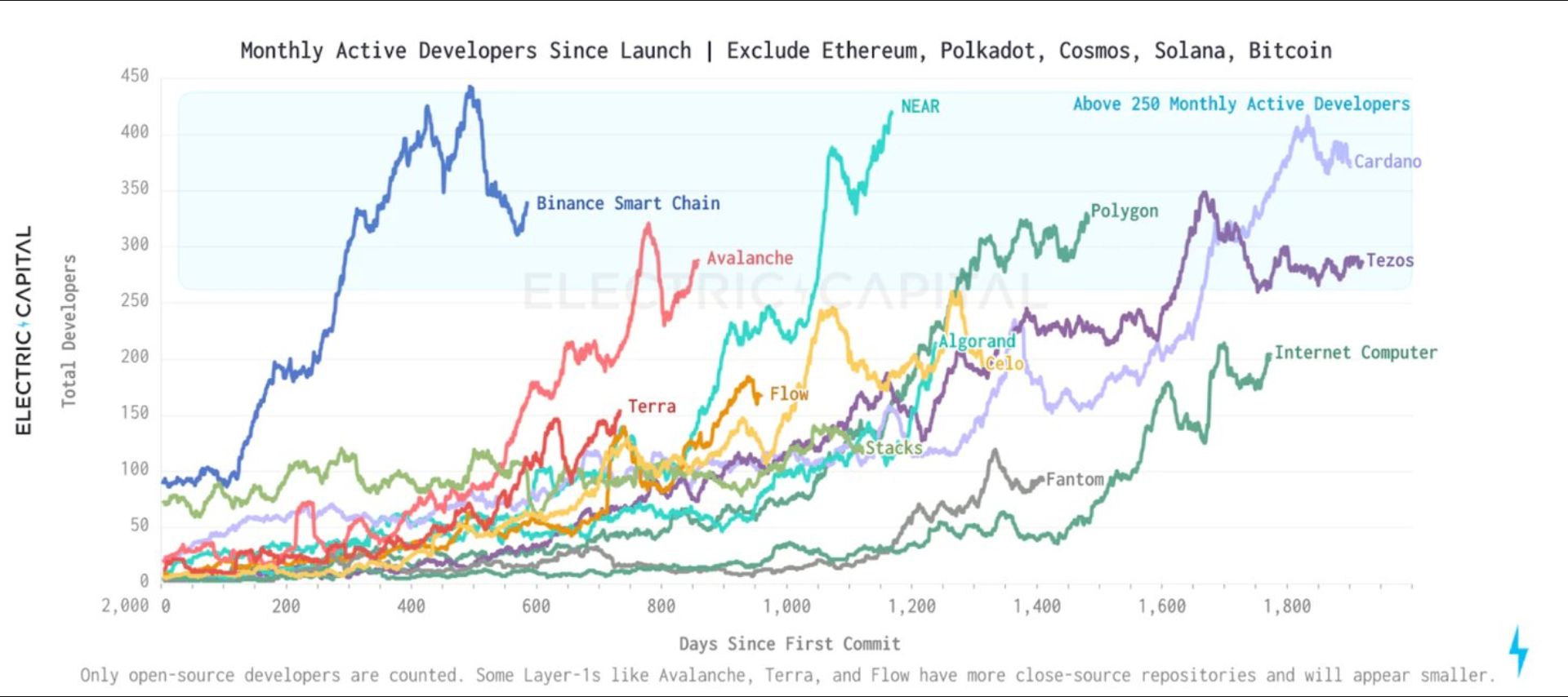
Source: Twitter
4. Usage
This must be the most important part of all. But not only this, are users willing to pay for the services rendered? In other words, will they pay for using the apps? So, here are the gas fees.
The cheaper the gas fees, the more popular a blockchain will be. Ethereum has its L2 solutions. All the Ethereum killers have their unique solutions. Bottom line is that everybody likes low-cost gas fees. Here is a comparison chart of fees in layer 1 blockchains:
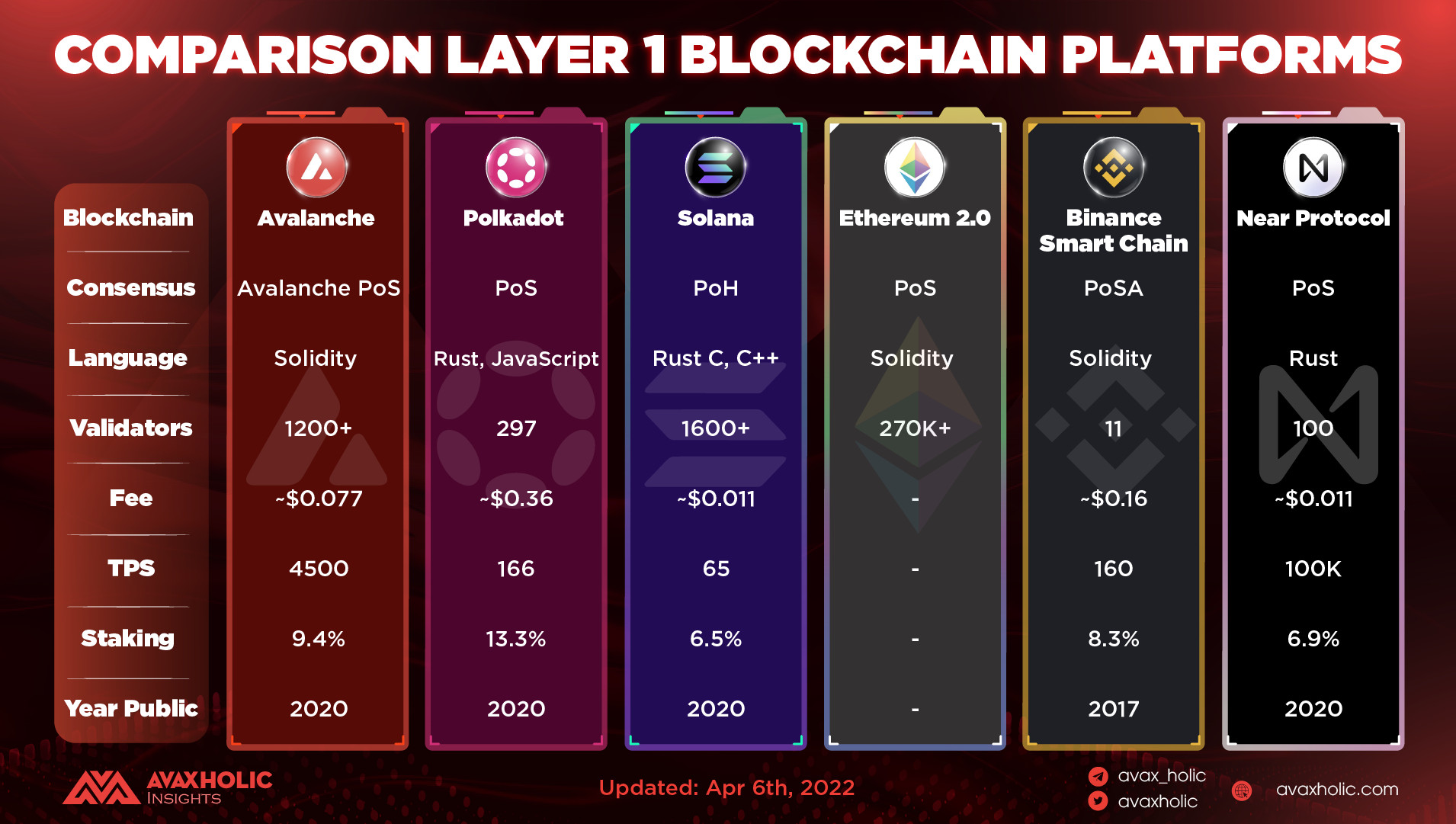
Source: Twitter
5. Profitability
To see if a chain is profitable, you need to compare two indicators.
-
How much is the blockchain paying for security?
Chains use hash rate, to secure their chains, which costs money. So, this gives you an idea of how much they spend on security. For instance, BTC currently measures the hash rate in Exahashes. This is quantillions of Hashes per second. That’s the next step up from quadrillions.
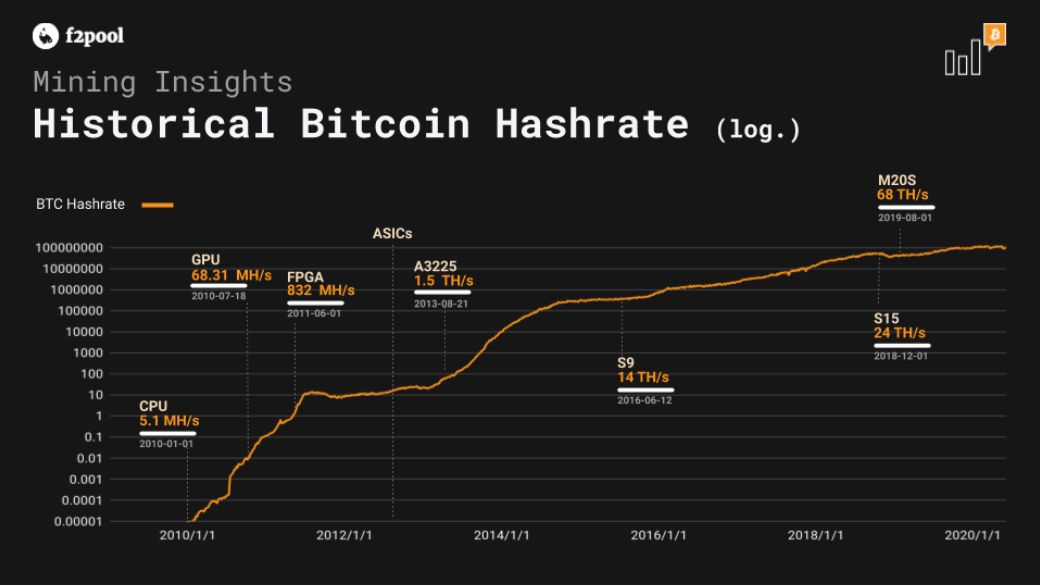
Source: Buybitcoinworldwide
-
How much does a blockchain generate in revenue?
There are some ways that a blockchain can generate profit. Here they are:
- Develop software solutions that have specific purposes.
- Provide one or more software services.
- Transaction fees generate income.
- Contract agreements.
- Speculating on cryptocurrencies.
Now, how useful the last point is, is debatable. However, a coin or token that appreciates, is, in general, good for a chain.
Conclusion
Here are 5 good ways to find out if a layer 1 blockchain is going to make it. A blockchain must be secure and decentralized. Furthermore, it needs developers to build apps and users of the chain. At last, a blockchain must be profitable.
However, this depends on many factors, for example, gas fees. It is an important question, though. Who builds during this bear market sets himself up to be among the winners in the next bull market.
 altcoinbuzz.io
altcoinbuzz.io