Traditional financial systems might get transformed to DeFi due to its ability to provide various financial services in a decentralized manner. People are using DeFi products without the need of any third parties such as banks and other financial institutions. Most of the big DeFi protocols are providing thousands of users with financial services. One of the leaders in the lending category, Aave is setting an example for other DeFi protocols to follow.
What Is Aave?
Aave is the eighth-largest DeFi protocol and second-largest lending protocol where users can lend or borrow cryptocurrencies. Lenders also earn interest on their deposited cryptocurrencies. Borrowers have to pay interest after borrowing cryptocurrency, and they have to put some cryptocurrency as collateral also.
Aave protocol is available on Ethereum, Polygon, Avalanche, Fantom, and Harmony, etc. networks for public use. The protocol has its own native token called AAVE. Moreover, AAVE is a governance token, and holders of AAVE tokens can participate and vote in governance proposals that give them the power to decide the future direction of the protocol collectively.
How Does Aave Works?
Lenders deposit their crypto assets into a lending pool of Aave and borrowers borrow from this pool. Aave follows pool-to-peer lending instead of peer-to-peer lending, where all the liquidity is stored on these pools. Lenders and borrowers deposit and borrow from these pools.
Borrowers have to pay interest on the loan, while lenders earn interest on their deposited assets. Borrowers need to put up collateral to take the loan amount. The collateral deposited must be greater than the borrowing amount. As loans are provided to borrowers without considering their line of credit and taking their personal details. So, to safeguard the assets deposited by lenders, protocol sells the borrower’s collateral when the borrower fails to pay back the loan amount with interest.
Lending Mechanism
Lenders deposit their assets into the pool and in exchange they receive atoken which equally represents their deposited amount.
Lenders can get their deposited assets back anytime by returning their atoken to the protocol. The atoken balance represents the deposited amount and the interest that accrued on the assets. Interest rates changes with borrowing demand on the protocol. When a lender returns atoken, they receive their deposited assets and interest accrued on them.
Borrowing Mechanism
Borrowers deposit their cryptocurrency assets into the pool as collateral for taking loans. In exchange, they can borrow the amount of an asset as defined by each collateral’s loan-to-value.
The maximum amount of cryptocurrency that can be borrowed by depositing specific collateral is defined by Loan-To-Value. It is expressed in percentage: at LTV=75%, after putting 1BTC worth of collateral, the user will be able to borrow 0.75BTC. After borrowing, LTV may change with market conditions.
Borrowers must return the borrowed assets with interest if they wish to close their position.
Tokenomics
The total supply of Aave tokens is 16 million tokens and 13.5 million AAVE tokens are currently in circulation. Around 3 million tokens are allocated to the Aave ecosystem reserve for protocol incentives. Aave holders decide how reserves of the ecosystem are allocated through governance.
Assets of Aave protocol are secured by the Safety module, tokens staked by AAVE holders act as insurance in case of any shortfall events. AAVE holders who stake their tokens are called stakers. Generally, stakers earn AAVE tokens as well as protocol fees as a safety incentive.
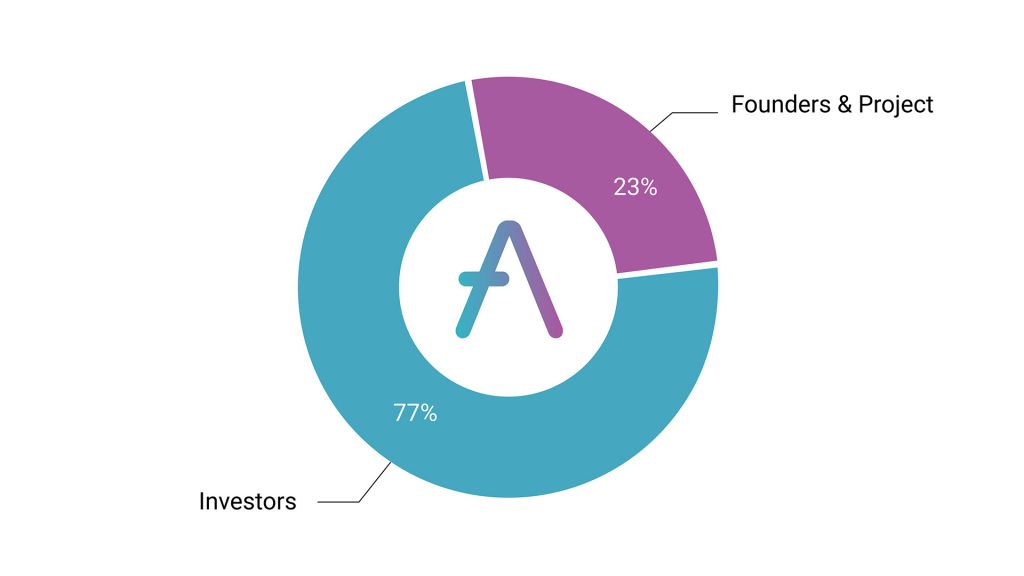
Fig. AAVE’s Initial Token Distribution
As of writing this article, the price of the AAVE token is 262 US dollars and the market cap is 3.52 billion US dollars. Total value locked, i.e., the total amount of cryptocurrency deposited in the protocol is worth 14.3 billion dollars.
Main Features of Aave protocol
A Large Number of Collaterals
Aave supports more than 20 different assets as collateral for borrowers such as DAI, ETH, BAT, LINK, MANA, MKR, SNX, USDT, etc.
Flash Loans
A flash loan enables users to borrow cryptocurrency without requiring collateral. Flash loans should be paid back in the same transaction. The transaction will fail if they do not reimburse.
Its use cases include arbitrage, collateral swapping, self-liquidation, and others.
Switching of Interest Rate
Aave protocol adjusts interest rate algorithmically on the basis of supply and demand, i.e., when the deposited amount by lenders increases, liquidity increase in the pool, interest rates decrease and borrowers have to pay less interest on their loans and when the borrowing demand increases, it reduces available liquidity, interest rates rise, and depositors generate more income. The protocol allows users to switch between stable and variable interest rates so that users can choose the best rate for them.
Conclusion
Aave protocol has set an example for other Defi protocols by its continued innovation in DeFi space. They have brought new features for their users with every major upgrade. Aave being on multiple chains have increased their user base in comparison to other lending protocols that are only on the Ethereum blockchain. It also provides its users with a variety of assets for lending and borrowing. Aave is providing way better interest rates to its users as compared to banks. In the future, more and more institutions may start using Aave to get a better interest rate on their assets.
 cryptoknowmics.com
cryptoknowmics.com